Development of Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assays Targeting Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)
- PMID: 32276051
- PMCID: PMC7144851
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2020.03.006
Development of Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assays Targeting Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)
Abstract
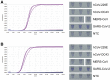
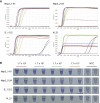
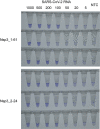
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic now has >2,000,000 confirmed cases worldwide. COVID-19 is currently diagnosed using quantitative RT-PCR methods, but the capacity of quantitative RT-PCR methods is limited by their requirement of high-level facilities and instruments. We developed and evaluated reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) assays to detect genomic RNA of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative virus of COVID-19. RT-LAMP assays reported in this study can detect as low as 100 copies of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Cross-reactivity of RT-LAMP assays to other human coronaviruses was not observed. A colorimetric detection method was adapted for this RT-LAMP assay to enable higher throughput.
Copyright © 2020 Association for Molecular Pathology and American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Zhou P., Yang X.L., Wang X.G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Si H.R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C.L., Chen H.D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., Jiang R.D., Liu M.Q., Chen Y., Shen X.R., Wang X., Zheng X.S., Zhao K., Chen Q.J., Deng F., Liu L.L., Yan B., Zhan F.X., Wang Y.Y., Xiao G.F., Shi Z.L. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020;579:270–273. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu N., Zhang D., Wang W., Li X., Yang B., Song J., Zhao X., Huang B., Shi W., Lu R., Niu P., Zhan F., Ma X., Wang D., Xu W., Wu G., Gao G.F., Tan W., China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:727–733. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang C., Wang Y., Li X., Ren L., Zhao J., Hu Y., Zhang L., Fan G., Xu J., Gu X., Cheng Z., Yu T., Xia J., Wei Y., Wu W., Xie X., Yin W., Li H., Liu M., Xiao Y., Gao H., Guo L., Xie J., Wang G., Jiang R., Gao Z., Jin Q., Wang J., Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497–506. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corman V.M., Landt O., Kaiser M., Molenkamp R., Meijer A., Chu D.K., Bleicker T., Brunink S., Schneider J., Schmidt M.L., Mulders D.G., Haagmans B.L., van der Veer B., van den Brink S., Wijsman L., Goderski G., Romette J.L., Ellis J., Zambon M., Peiris M., Goossens H., Reusken C., Koopmans M.P., Drosten C. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill. 2020;25:2000045. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

