Human Clinical Relevance of the Porcine Model of Pseudoallergic Infusion Reactions
- PMID: 32276476
- PMCID: PMC7235862
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines8040082
Human Clinical Relevance of the Porcine Model of Pseudoallergic Infusion Reactions
Abstract
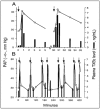
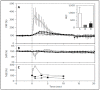
Pigs provide a highly sensitive animal model for pseudoallergic infusion reactions, which are mild-to-severe hypersensitivity reactions (HSRs) that arise following intravenous administration of certain nanoparticulate drugs (nanomedicines) and other macromolecular structures. This model has been used in research for three decades and was also proposed by regulatory bodies for preclinical assessment of the risk of HSRs in the clinical stages of nano-drug development. However, there are views challenging the human relevance of the model and its utility in preclinical safety evaluation of nanomedicines. The argument challenging the model refers to the "global response" of pulmonary intravascular macrophages (PIM cells) in the lung of pigs, preventing the distinction of reactogenic from non-reactogenic particles, therefore overestimating the risk of HSRs relative to its occurrence in the normal human population. The goal of this review is to present the large body of experimental and clinical evidence negating the "global response" claim, while also showing the concordance of symptoms caused by different reactogenic nanoparticles in pigs and hypersensitive man. Contrary to the model's demotion, we propose that the above features, together with the high reproducibility of quantifiable physiological endpoints, validate the porcine "complement activation-related pseudoallergy" (CARPA) model for safety evaluations. However, it needs to be kept in mind that the model is a disease model in the context of hypersensitivity to certain nanomedicines. Rather than toxicity screening, its main purpose is specific identification of HSR hazard, also enabling studies on the mechanism and mitigation of potentially serious HSRs.
Keywords: adverse drug reactions; anaphylactoid reactions; anaphylaxis; complement; nanomedicine; nanoparticle; pigs; pulmonary intravascular macrophages; shock.
Conflict of interest statement
J.S. is employed by SeroScience LLC, an immune toxicological CRO providing, among others, the pig tests discussed in the review. R.B. is president at Bawa Biotech LLC, a biotech/pharma consultancy and patent law firm, and Chief IP Counsel at Guanine Inc. He is a scientific advisor to Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Israel.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Complement activation-related pseudoallergy: a stress reaction in blood triggered by nanomedicines and biologicals.Mol Immunol. 2014 Oct;61(2):163-73. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2014.06.038. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Mol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25124145 Review.
-
A porcine model of complement-mediated infusion reactions to drug carrier nanosystems and other medicines.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012 Dec;64(15):1706-16. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.07.005. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012. PMID: 22820530 Review.
-
Evaluation of the Acute Anaphylactoid Reactogenicity of Nanoparticle-Containing Medicines and Vaccines Using the Porcine CARPA Model.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2789:229-243. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3786-9_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38507008
-
The Critical Choice of Animal Models in Nanomedicine Safety Assessment: A Lesson Learned From Hemoglobin-Based Oxygen Carriers.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 26;11:584966. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.584966. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33193403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complement activation-related pseudoallergy: a new class of drug-induced acute immune toxicity.Toxicology. 2005 Dec 15;216(2-3):106-21. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2005.07.023. Epub 2005 Sep 2. Toxicology. 2005. PMID: 16140450 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of a translational swine model of respiratory hypersensitivity induced by exposure to Phleum pratense pollen allergens.Front Allergy. 2025 Apr 7;6:1557656. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2025.1557656. eCollection 2025. Front Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40259949 Free PMC article.
-
How to Perform Cardiac Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (cCEUS): Part I.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jul 9;15(14):1743. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15141743. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Nanoparticles for Nucleic Acid Delivery to Endothelial Cells.Pharm Res. 2023 Jan;40(1):3-25. doi: 10.1007/s11095-023-03471-7. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Pharm Res. 2023. PMID: 36735106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biocompatibility of Water-Dispersible Pristine Graphene and Graphene Oxide Using a Close-to-Human Animal Model: A Pilot Study on Swine.Adv Healthc Mater. 2025 Apr;14(10):e2401783. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202401783. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025. PMID: 39385652 Free PMC article.
-
A naturally hypersensitive porcine model may help understand the mechanism of COVID-19 mRNA vaccine-induced rare (pseudo) allergic reactions: complement activation as a possible contributing factor.Geroscience. 2022 Apr;44(2):597-618. doi: 10.1007/s11357-021-00495-y. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Geroscience. 2022. PMID: 35146583 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

