Clinical spectrum, genetic complexity and therapeutic approaches for retinal disease caused by ABCA4 mutations
- PMID: 32278709
- PMCID: PMC7544654
- DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100861
Clinical spectrum, genetic complexity and therapeutic approaches for retinal disease caused by ABCA4 mutations
Abstract
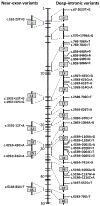
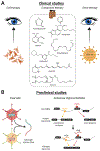
The ABCA4 protein (then called a "rim protein") was first identified in 1978 in the rims and incisures of rod photoreceptors. The corresponding gene, ABCA4, was cloned in 1997, and variants were identified as the cause of autosomal recessive Stargardt disease (STGD1). Over the next two decades, variation in ABCA4 has been attributed to phenotypes other than the classically defined STGD1 or fundus flavimaculatus, ranging from early onset and fast progressing cone-rod dystrophy and retinitis pigmentosa-like phenotypes to very late onset cases of mostly mild disease sometimes resembling, and confused with, age-related macular degeneration. Similarly, analysis of the ABCA4 locus uncovered a trove of genetic information, including >1200 disease-causing mutations of varying severity, and of all types - missense, nonsense, small deletions/insertions, and splicing affecting variants, of which many are located deep-intronic. Altogether, this has greatly expanded our understanding of complexity not only of the diseases caused by ABCA4 mutations, but of all Mendelian diseases in general. This review provides an in depth assessment of the cumulative knowledge of ABCA4-associated retinopathy - clinical manifestations, genetic complexity, pathophysiology as well as current and proposed therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: ABCA4-associated retinopathy; Allelic heterogeneity; Autofluorescence; Hypomorphic variant; Penetrance; Phenocopies; Pseudoexon; Splice defects; Stargardt disease; Structural variant; Therapy.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Acland GM, Aguirre GD, Ray J, Zhang Q, Aleman TS, Cideciyan AV, Pearce-Kelling SE, Anand V, Zeng Y, Maguire AM, Jacobson SG, Hauswirth WW, Bennett J, 2001. Gene therapy restores vision in a canine model of childhood blindness. Nat. Genet 28, 92–95. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre-Lamban J, Gonzalez-Aguilera JJ, Riveiro-Alvarez R, Cantalapiedra D, Avila-Fernandez A, Villaverde-Montero C, Corton M, Bianco-Kelly F, Garcia-Sandoval B, Ayuso C, 2011. Further associations between mutations and polymorphisms in the ABCA4 gene: clinical implication of allelic variants and their role as protector/risk factors. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci 52, 6206–6212. - PubMed
-
- Ahn J, Molday RS, 2000. Purification and characterization of ABCR from bovine rod outer segments. Methods Enzymol. 315, 864–879. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

