Restructuring Structural Heart Disease Practice During the COVID-19 Pandemic: JACC Review Topic of the Week
- PMID: 32278716
- PMCID: PMC7146690
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.009
Restructuring Structural Heart Disease Practice During the COVID-19 Pandemic: JACC Review Topic of the Week
Abstract
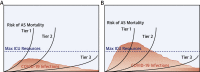
Patients with structural heart disease are at increased risk of adverse outcomes from the coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) due to advanced age and comorbidity. In the midst of a global pandemic of a novel infectious disease, reality-based considerations comprise an important starting point for formulating clinical management pathways. The aims of these "crisis-driven" recommendations are: 1) to ensure appropriate and timely treatment of structural heart disease patients; 2) to minimize the risk of COVID-19 exposure to patients and health care workers; and 3) to limit resource utilization under conditions of constraint. Although the degree of disruption to usual practice will vary across the United States and elsewhere, we hope that early experiences from a heart team operating in the current global epicenter of COVID-19 may prove useful for others adapting their practice in advance of local surges of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; heart team; structural heart disease; valve center.
Copyright © 2020 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Maddox T.M., Stecker E.C., Bozkurt B. 2020. ACC Clinical Bulletin COVID-19 Clinical Guidance for the Cardiovascular Care Team.https://www.acc.org/∼/media/665AFA1E710B4B3293138D14BE8D1213.pdf Available at:
-
- Clerkin K.J., Fried J.A., Raikhelkar J. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2020 Mar 21 [E-pub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Wu Z., McGoogan J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020 Feb 24 [E-pub ahead of print] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

