Tumour mutational burden as a biomarker for immunotherapy: Current data and emerging concepts
- PMID: 32278982
- PMCID: PMC9473693
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.02.038
Tumour mutational burden as a biomarker for immunotherapy: Current data and emerging concepts
Abstract
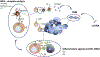
Treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors targeting programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) or its ligand (PD-L1) can generate durable responses in various cancer types, but only in a subset of patients. The use of predictive biomarkers for response to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors is critical for patient selection. Expression of PD-L1 has demonstrated utility in patient selection. Tumour mutational burden (TMB) is an emerging biomarker for response to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. The evaluation of this biomarker is based on the hypothesis that a high number of mutations in somatic exonic regions will lead to an increase in neoantigen production, which could then be recognised by CD8+ T cells, resulting in improved immune responses. In this review, we will discuss rationale and implementation of TMB usage in patients, development of different methods to assess it, current limitations and technical issues to use this biomarker as a diagnostic test and propose future perspectives beyond TMB.
Keywords: Biomarker; Immunotherapy; Tumour mutational burden.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Gandhi L, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S, Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F, et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 31 mai 2018;378(22):2078–92. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG, Hui R, Csőszi T, Fülöp A, et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1–positive non–small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 10 nov 2016;375(19):1823–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

