Ibrutinib-Associated Cardiac Tamponade with Concurrent Antiplatelet Therapy
- PMID: 32280549
- PMCID: PMC7139853
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4282486
Ibrutinib-Associated Cardiac Tamponade with Concurrent Antiplatelet Therapy
Abstract
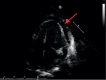
Ibrutinib is approved for the first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). A well-known side effect of ibrutinib therapy is increased bleeding risk, which ranges from mild mucocutaneous bleeding to rarely life-threatening hemorrhage. The increased bleeding tendency associated with ibrutinib is thought to be related to its effect on several platelet signaling pathways, which can be exacerbated in the setting of concurrent antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapy. We present an 82-year-old male with CLL on ibrutinib and concurrent antiplatelet therapy who developed cardiac tamponade due to a hemorrhagic pericardial effusion requiring emergent placement of a pericardial window. This case further highlights the risk of major bleeding in patients treated with ibrutinib and concurrent antiplatelet therapy.
Copyright © 2020 Jennifer L. Miatech et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

