U.S. Food and Drug Administration-Certified Food Dyes as Organocatalysts in the Visible Light-Promoted Chlorination of Aromatics and Heteroaromatics
- PMID: 32280913
- PMCID: PMC7144131
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00631
U.S. Food and Drug Administration-Certified Food Dyes as Organocatalysts in the Visible Light-Promoted Chlorination of Aromatics and Heteroaromatics
Abstract
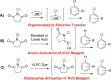
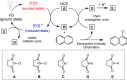
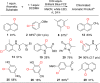
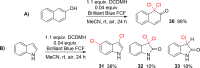
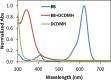
Seven FDA-certified food dyes have been investigated as organocatalysts. As a result, Fast Green FCF and Brilliant Blue FCF have been discovered as catalysts for the chlorination of a wide range of arenes and heteroarenes in moderate to excellent yields and high regioselectivity. Mechanistic investigations of the separate systems indicate that different modes of activation are in operation, with Fast Green FCF being a light-promoted photoredox catalyst that is facilitating a one-electron oxidation of N-chlorosuccinimide (NCS) and Brilliant Blue FCF serving as a chlorine-transfer catalyst in its sulfonphthalein form with 1,3-dichloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin (DCDMH) as stoichiometric chlorine source. Dearomatization of naphthol and indole substrates was observed in some examples using the Brilliant Blue/DCDMH system.
Copyright © 2020 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Dalko P. I.; Moisan L. In the golden age of organocatalysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5138–5175. 10.1002/anie.200400650. - DOI - PubMed
- Bertelsen S.; Jørgensen K. A. Organocatalysis--after the gold rush. Chem. Soc. Rev 2009, 38, 2178–2189. 10.1039/b903816g. - DOI - PubMed
- Alemán J.; Cabrera S. Applications of asymmetric organocatalysis in medicinal chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev 2013, 42, 774–793. 10.1039/C2CS35380F. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Constable D. J. C.; Dunn P. J.; Hayler J. D.; Humphrey G. R.; Leazer J. L. Jr.; Linderman R. J.; Lorenz K.; Manley J.; Pearlman B. A.; Wells A.; Zaks A.; Zhang T. Y. Key green chemistry research areas—a perspective from pharmaceutical manufacturers. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 411–420. 10.1039/B703488C. - DOI
-
- Wilcken R.; Zimmermann M. O.; Lange A.; Joerger A. C.; Boeckler F. M. Principles and applications of halogen bonding in medicinal chemistry and chemical biology. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1363–1388. 10.1021/jm3012068. - DOI - PubMed
- Cernak T.; Dykstra K. D.; Tyagarajan S.; Vachal P.; Krska S. W. The medicinal chemist’s toolbox for late stage functionalization of drug-like molecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 546–576. 10.1039/C5CS00628G. - DOI - PubMed
- Petrone D. A.; Ye J.; Lautens M. Modern Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Carbon-Halogen Bond Formation. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 8003–8104. 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00089. - DOI - PubMed
- Zha G.-F.; Qin H.-L.; Kantchev E. A. B. Ruthenium-catalyzed direct arylations with aryl chlorides. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 30875–30885. 10.1039/C6RA02742C. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

