Proximal Humerus Tumors: Higher-than-Expected Risk of Revision With Constrained Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
- PMID: 32281773
- PMCID: PMC7571930
- DOI: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001245
Proximal Humerus Tumors: Higher-than-Expected Risk of Revision With Constrained Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
Abstract
Background: The treatment of proximal humerus tumors with endoprostheses is associated with a high risk of implant-related surgical complications. Because of extensive soft-tissue resection and muscular detachment during surgery, instability is the most common serious complication. A reverse total shoulder arthroplasty with a highly constrained design is one option to mitigate instability, but few studies have reported the results of this prosthesis for proximal humerus tumor resections.
Questions/purposes: (1) What are the short-term functional results of the constrained reverse total shoulder prosthesis in terms of Musculoskeletal Tumor Society (MSTS), DASH, and Constant-Murley scores and ROM values? (2) What is the frequency of revision, using a competing-risks estimator to assess implant survival, and what were the causes of the revisions that occurred? (3) What proportion of patients experienced dislocations at short-term follow-up?
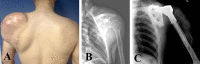
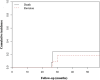
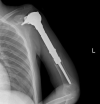
Methods: Between January 2014 and June 2017, we treated 55 patients with proximal humeral resections and reconstructions for malignant tumors. Of those, 33% (18) of patients were treated with the constrained, reverse total shoulder arthroplasty implant under study here. During that period, no other constrained reverse total shoulder implant was used; however, 13% (seven) of patients were treated with conventional (unconstrained) reverse total shoulder implants, 27% (15) had hemiarthroplasties, 15% (eight) of patients had biologic reconstructions with auto- or allografts and 13% (seven) underwent amputation. During the period in question, our general indications for use of the constrained device under study here were resection of the deltoid muscle/axillary nerve or the deltoid insertion on the humerus due to tumor invasion, or extensive rotator cuff and surrounding soft tissue resection that might result in shoulder instability. During this period, these indications were adhered to consistently. Four of 18 patients treated with the study implant died (three died with the implant intact) and none were lost to follow-up before 2 years, leaving 14 patients (seven women and seven men) for study at a median (range) follow-up of 35 months (25 to 65). Two authors evaluated the clinical and functional status of each patient with ROM (flexion, extension, internal and external rotation, abduction, and adduction) and MSTS, (range 0% to 100%), Constant-Murley (range 0% to 100%), and DASH (range 0 points to 100 points) scores. For the MSTS and Constant-Murley scores, higher percentage scores mean better functional outcome; and for the DASH score, a higher score means more severe disability. Radiographs were obtained at each visit and were used to look for signs of loosening, which we defined as progressive radiolucencies between visits, prosthetic component migration, and fragmentation/fracture of the cement. The Sirveaux classification was used to determine scapular notching. A competing risks analysis with 95% confidence intervals was performed to estimate the cumulative incidence of revision surgery, which we defined as any reoperation in which the implant was removed or changed for any reason, with patient mortality as a competing event.
Results: At the most recent follow-up, the median (range) MSTS score was 78% (50 to 90), the DASH score was 20 (8 to 65), and the Constant-Murley score was 53% (26 to 83). The median ROM was 75° in forward flexion (40 to 160), 78° in abduction (30 to 150), 35° in internal rotation (10 to 80), and 33° in external rotation (0 to 55). Postoperatively, two of 14 patients underwent or were supposed to undergo revision surgery, and the cumulative incidence of revision surgery was 18% for both 30 and 48 months (95% CI 2 to 45). During the study period, no patients reported instability, and no dislocations occurred.
Conclusions: Our findings are concerning because the revision risk with this constrained reverse total shoulder implant was higher than has been reported by others for other proximal humerus prostheses. The highly constrained design that helps prevent instability might also transmit increased stresses to the humeral component-bone interface, therefore making it susceptible to loosening. We believe that any other implant with a similar degree of constraint will have the same problem, and changing the indications for patient selection may not solve this issue. These theories need to be tested biomechanically, but our desire is to warn surgeons that while trying to prevent instability, one might trade one complication (instability) for another: aseptic loosening.
Level of evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study.
Conflict of interest statement
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and
Figures

Comment in
-
CORR Insights®: Proximal Humerus Tumors: Higher-than-Expected Risk of Revision With Constrained Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020 Nov;478(11):2596-2597. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001308. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020. PMID: 33112584 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Abdeen A, Hoang BH, Athanasian EA, Morris CD, Boland PJ, Healey JH. Allograft-prosthesis composite reconstruction of the proximal part of the humerus: functional outcome and survivorship. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:2406-2415. - PubMed
-
- Bilgin SS. Reconstruction of proximal humeral defects with shoulder arthrodesis using free vascularized fibular graft. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94:e94. - PubMed
-
- Bonnevialle N, Mansat P, Lebon J, Laffosse JM, Bonnevialle P. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for malignant tumors of proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24:36-44. - PubMed
-
- Cannon CP, GU Paraliticci, Lin PP, Lewis VO, Yasko AW. Functional outcome following endoprosthetic reconstruction of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18:705-710. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

