Intestinal restriction of Salmonella Typhimurium requires caspase-1 and caspase-11 epithelial intrinsic inflammasomes
- PMID: 32282854
- PMCID: PMC7179941
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008498
Intestinal restriction of Salmonella Typhimurium requires caspase-1 and caspase-11 epithelial intrinsic inflammasomes
Abstract
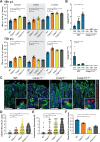
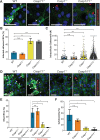
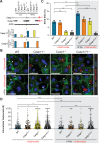
We investigated the role of the inflammasome effector caspases-1 and -11 during Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection of murine intestinal epithelial cells (IECs). Salmonella burdens were significantly greater in the intestines of caspase-1/11 deficient (Casp1/11-/-), Casp1-/- and Casp11-/- mice, as compared to wildtype mice. To determine if this reflected IEC-intrinsic inflammasomes, enteroid monolayers were derived and infected with Salmonella. Casp11-/- and wildtype monolayers responded similarly, whereas Casp1-/- and Casp1/11-/- monolayers carried significantly increased intracellular burdens, concomitant with marked decreases in IEC shedding and death. Pretreatment with IFN-γ to mimic inflammation increased caspase-11 levels and IEC death, and reduced Salmonella burdens in Casp1-/- monolayers, while high intracellular burdens and limited cell shedding persisted in Casp1/11-/- monolayers. Thus caspase-1 regulates inflammasome responses in IECs at baseline, while proinflammatory activation of IECs reveals a compensatory role for caspase-11. These results demonstrate the importance of IEC-intrinsic canonical and non-canonical inflammasomes in host defense against Salmonella.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

