Hematological findings and complications of COVID-19
- PMID: 32282949
- PMCID: PMC7262337
- DOI: 10.1002/ajh.25829
Hematological findings and complications of COVID-19
Abstract
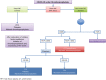
COVID-19 is a systemic infection with a significant impact on the hematopoietic system and hemostasis. Lymphopenia may be considered as a cardinal laboratory finding, with prognostic potential. Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and peak platelet/lymphocyte ratio may also have prognostic value in determining severe cases. During the disease course, longitudinal evaluation of lymphocyte count dynamics and inflammatory indices, including LDH, CRP and IL-6 may help to identify cases with dismal prognosis and prompt intervention in order to improve outcomes. Biomarkers, such high serum procalcitonin and ferritin have also emerged as poor prognostic factors. Furthermore, blood hypercoagulability is common among hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Elevated D-Dimer levels are consistently reported, whereas their gradual increase during disease course is particularly associated with disease worsening. Other coagulation abnormalities such as PT and aPTT prolongation, fibrin degradation products increase, with severe thrombocytopenia lead to life-threatening disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), which necessitates continuous vigilance and prompt intervention. So, COVID-19 infected patients, whether hospitalized or ambulatory, are at high risk for venous thromboembolism, and an early and prolonged pharmacological thromboprophylaxis with low molecular weight heparin is highly recommended. Last but not least, the need for assuring blood donations during the pandemic is also highlighted.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
No relevant conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Comment in
-
Lymphopenia in critically ill COVID-19 patients: A predictor factor of severity and mortality.Int J Lab Hematol. 2021 Feb;43(1):e38-e40. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.13351. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Int J Lab Hematol. 2021. PMID: 32996680 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the chinese center for disease control and prevention. JAMA. 2020;323:1239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous