Rapid and severe Covid-19 pneumonia with severe acute chest syndrome in a sickle cell patient successfully treated with tocilizumab
- PMID: 32282956
- PMCID: PMC7262334
- DOI: 10.1002/ajh.25833
Rapid and severe Covid-19 pneumonia with severe acute chest syndrome in a sickle cell patient successfully treated with tocilizumab
Conflict of interest statement
Bartolucci reports being a consultant for F. Hoffmann‐La Roche. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this letter was reported.
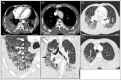
Figures
Comment in
-
Dramatic improvement after tocilizumab of severe COVID-19 in a child with sickle cell disease and acute chest syndrome.Am J Hematol. 2020 Aug;95(8):E192-E194. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25855. Epub 2020 May 16. Am J Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32358817 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bulletin épidémiologique hebdomadaire [Internet]. http://beh.santepubliquefrance.fr/beh/2015/8/2015_8_2.html. Accessed April 3, 2020.
-
- Vichinsky EP, Neumayr LD, Earles AN, et al. Causes and outcomes of the acute chest syndrome in sickle cell disease. National Acute Chest Syndrome Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(25):1855‐1865. - PubMed
-
- Boissier F, Bagate F, Schmidt M, et al. Extracorporeal Life Support for Severe Acute Chest Syndrome in Adult Sickle Cell Disease: A Preliminary Report. Crit Care Med. 2019;47(3):e263‐e265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
