Early impact of COVID-19 on transplant center practices and policies in the United States
- PMID: 32282982
- PMCID: PMC7262146
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15915
Early impact of COVID-19 on transplant center practices and policies in the United States
Abstract
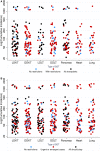
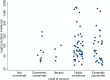
COVID-19 is a novel, rapidly changing pandemic: consequently, evidence-based recommendations in solid organ transplantation (SOT) remain challenging and unclear. To understand the impact on transplant activity across the United States, and center-level variation in testing, clinical practice, and policies, we conducted a national survey between March 24, 2020 and March 31, 2020 and linked responses to the COVID-19 incidence map. Response rate was a very high 79.3%, reflecting a strong national priority to better understand COVID-19. Complete suspension of live donor kidney transplantation was reported by 71.8% and live donor liver by 67.7%. While complete suspension of deceased donor transplantation was less frequent, some restrictions to deceased donor kidney transplantation were reported by 84.0% and deceased donor liver by 73.3%; more stringent restrictions were associated with higher regional incidence of COVID-19. Shortage of COVID-19 tests was reported by 42.5%. Respondents reported a total of 148 COVID-19 recipients from <1 to >10 years posttransplant: 69.6% were kidney recipients, and 25.0% were critically ill. Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) was used by 78.1% of respondents; azithromycin by 46.9%; tocilizumab by 31.3%, and remdesivir by 25.0%. There is wide heterogeneity in center-level response across the United States; ongoing national data collection, expert discussion, and clinical studies are critical to informing evidence-based practices.
Keywords: clinical decision-making; epidemiology; guidelines; infectious agents-viral.
© 2020 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures


References
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323(13):1239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AI007291/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK117563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32DK117563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK101677/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32DK113719/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32AI007291/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK115908/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01DK101677/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK101828/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32DK007713-22/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23DK115908/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24DK101828/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK113719/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

