Evolutionary analysis of SARS-CoV-2: how mutation of Non-Structural Protein 6 (NSP6) could affect viral autophagy
- PMID: 32283146
- PMCID: PMC7195303
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.058
Evolutionary analysis of SARS-CoV-2: how mutation of Non-Structural Protein 6 (NSP6) could affect viral autophagy
Abstract
Background: SARS-CoV-2 is a new coronavirus that has spread globally, infecting more than 150000 people, and being declared pandemic by the WHO. We provide here bio-informatic, evolutionary analysis of 351 available sequences of its genome with the aim of mapping genome structural variations and the patterns of selection.
Methods: A Maximum likelihood tree has been built and selective pressure has been investigated in order to find any mutation developed during the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic that could potentially affect clinical evolution of the infection.
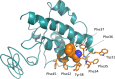
Finding: We have found in more recent isolates the presence of two mutations affecting the Non-Structural Protein 6 (NSP6) and the Open Reding Frame10 (ORF 10) adjacent regions. Amino acidic change stability analysis suggests both mutations could confer lower stability of the protein structures.
Interpretation: One of the two mutations, likely developed within the genome during virus spread, could affect virus intracellular survival. Genome follow-up of SARS-CoV-2 spread is urgently needed in order to identify mutations that could significantly modify virus pathogenicity.
Keywords: Autophagy; Bio-informatic; COVID-19; Coronavirus; Molecular evolution; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest We declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Na Z., Dingyu Z., Wenling W. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020 doi: 10.1056/nejmoa2001017. https://doi.org/ - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hall T.A. BioEdit A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999;41:95–98.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

