Adoption of personal protective measures by ordinary citizens during the COVID-19 outbreak in Japan
- PMID: 32283285
- PMCID: PMC7194542
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.04.014
Adoption of personal protective measures by ordinary citizens during the COVID-19 outbreak in Japan
Abstract
Objectives: To clarify the implementation status of personal protective measures by ordinary citizens in Japan during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study based on internet-based survey. A total of 2400 people (50% male: 20-79 years) were selected between February 25 and 27, 2020, from registrants of an Internet research company, to complete a questionnaire. Participants were asked to indicate how often they implemented the following five personal protective measures recommended by the World Health Organization (hand hygiene, social distancing measures, avoiding touching the eyes, nose and mouth, respiratory etiquette, and self-isolation). In addition, the participants responded to questions regarding the daily frequency of hand hygiene events.
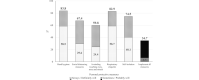
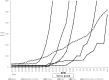
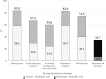
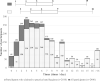
Results: The prevalence of the five personal protective measures ranged from 59.8% to 83.8%, with the lowest being avoiding touching the eyes, nose, and mouth. In total, 34.7% implemented all personal protective measures. The median daily hand hygiene events were 5 per day (25th percentile, 75th percentile: 3,8).
Conclusions: The protective measures implemented by ordinary citizens are insufficient and further public awareness activities are required.
Keywords: COVID-19; Epidemiology; Outbreak; Prevention; Protective measures; Public health.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Atchison C., Bowman L., Eaton J.W., Imai N., Redd R., Pristera P. 2020. Public Response to UK Government Recommendations on COVID-19: Population Survey, 17–18 March 2020. https://www.imperial.ac.uk/media/imperial-college/medicine/sph/ide/gida-... (accessed 22.03.20)
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) 2020. Guidelines for the use of non-pharmaceutical measures to delay and mitigate the impact of 2019-nCoV. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/guidelines-use-non-pharm... (accessed 22.03.20)
-
- Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (JMHLW) 2020. About coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/newpage_00032.html (accessed 22.03.20)
-
- Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (JMHLW) 2020. Basic policy on prevention of new coronavirus infection. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10900000/000599698.pdf (accessed 22.03.20) (Only Japanese)
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

