scRNA-seq Profiling of Human Testes Reveals the Presence of the ACE2 Receptor, A Target for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Spermatogonia, Leydig and Sertoli Cells
- PMID: 32283711
- PMCID: PMC7226809
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9040920
scRNA-seq Profiling of Human Testes Reveals the Presence of the ACE2 Receptor, A Target for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Spermatogonia, Leydig and Sertoli Cells
Abstract
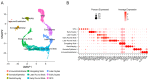
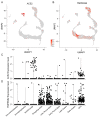
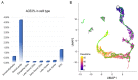
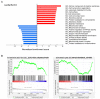
In December 2019, a novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) was identified in COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China. SARS-CoV-2 shares both high sequence similarity and the use of the same cell entry receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV). Several studies have provided bioinformatic evidence of potential routes of SARS-CoV-2 infection in respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and urinary systems. However, whether the reproductive system is a potential target of SARS-CoV-2 infection has not yet been determined. Here, we investigate the expression pattern of ACE2 in adult human testes at the level of single-cell transcriptomes. The results indicate that ACE2 is predominantly enriched in spermatogonia and Leydig and Sertoli cells. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) indicates that Gene Ontology (GO) categories associated with viral reproduction and transmission are highly enriched in ACE2-positive spermatogonia, while male gamete generation related terms are downregulated. Cell-cell junction and immunity-related GO terms are increased in ACE2-positive Leydig and Sertoli cells, but mitochondria and reproduction-related GO terms are decreased. These findings provide evidence that the human testis is a potential target of SARS-CoV-2 infection, which may have significant impact on our understanding of the pathophysiology of this rapidly spreading disease.
Keywords: ACE2; SARS-CoV-2; infection; scRNA-seq; spermatogonia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chen N., Zhou M., Dong X., Qu J., Gong F., Han Y., Qiu Y., Wang J., Liu Y., Wei Y., et al. Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of 99 Cases of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A Descriptive Study. Lancet. 2020;395:507–513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan J.F., Yuan S., Kok K.H., To K.K., Chu H., Yang J., Xing F., Liu J., Yip C.C., Poon R.W., et al. A Familial Cluster of Pneumonia Associated with the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Indicating Person-to-Person Transmission: A Study of a Family Cluster. Lancet. 2020;395:514–523. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann M., Kleine-Weber H., Schroeder S., Krüger N., Herrler T., Erichsen S., Schiergens T.S., Herrler G., Wu N.H., Nitsche A., et al. Sars-Cov-2 Cell Entry Depends on Ace2 and Tmprss2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

