TWINKLE and Other Human Mitochondrial DNA Helicases: Structure, Function and Disease
- PMID: 32283748
- PMCID: PMC7231222
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11040408
TWINKLE and Other Human Mitochondrial DNA Helicases: Structure, Function and Disease
Abstract
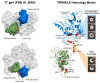
Mammalian mitochondria contain a circular genome (mtDNA) which encodes subunits of the oxidative phosphorylation machinery. The replication and maintenance of mtDNA is carried out by a set of nuclear-encoded factors-of which, helicases form an important group. The TWINKLE helicase is the main helicase in mitochondria and is the only helicase required for mtDNA replication. Mutations in TWINKLE cause a number of human disorders associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, neurodegeneration and premature ageing. In addition, a number of other helicases with a putative role in mitochondria have been identified. In this review, we discuss our current knowledge of TWINKLE structure and function and its role in diseases of mtDNA maintenance. We also briefly discuss other potential mitochondrial helicases and postulate on their role(s) in mitochondria.
Keywords: PEO; TWINKLE; mitochondria; mtDNA; replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
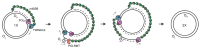




References
-
- Gray H., Wong T.W. Purification and identification of subunit structure of the human mitochondrial DNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 1992;267:5835–5841. - PubMed
-
- Fan L., Kim S., Farr C.L., Schaefer K.T., Randolph K.M., Tainer J.A., Kaguni L.S. A novel processive mechanism for DNA synthesis revealed by structure, modeling and mutagenesis of the accessory subunit of human mitochondrial DNA polymerase. J. Mol. Biol. 2006;358:1229–1243. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.02.073. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

