An RNA thermoswitch regulates daytime growth in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 32284544
- PMCID: PMC7231574
- DOI: 10.1038/s41477-020-0633-3
An RNA thermoswitch regulates daytime growth in Arabidopsis
Abstract
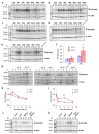
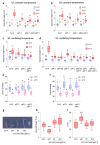
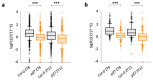
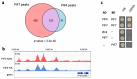
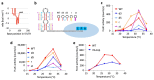
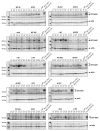
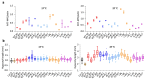
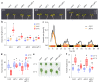
Temperature is a major environmental cue affecting plant growth and development. Plants often experience higher temperatures in the context of a 24 h day-night cycle, with temperatures peaking in the middle of the day. Here, we find that the transcript encoding the bHLH transcription factor PIF7 undergoes a direct increase in translation in response to warmer temperature. Diurnal expression of PIF7 transcript gates this response, allowing PIF7 protein to quickly accumulate in response to warm daytime temperature. Enhanced PIF7 protein levels directly activate the thermomorphogenesis pathway by inducing the transcription of key genes such as the auxin biosynthetic gene YUCCA8, and are necessary for thermomorphogenesis to occur under warm cycling daytime temperatures. The temperature-dependent translational enhancement of PIF7 messenger RNA is mediated by the formation of an RNA hairpin within its 5' untranslated region, which adopts an alternative conformation at higher temperature, leading to increased protein synthesis. We identified similar hairpin sequences that control translation in additional transcripts including WRKY22 and the key heat shock regulator HSFA2, suggesting that this is a conserved mechanism enabling plants to respond and adapt rapidly to high temperatures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





Comment in
-
Warm days, relaxed RNA.Nat Plants. 2020 May;6(5):438-439. doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0643-1. Nat Plants. 2020. PMID: 32284550 No abstract available.
References
-
- Quint M, et al. Molecular and genetic control of plant thermomorphogenesis. Nature Plants. 2016;2:15190. - PubMed
-
- Scheffers BR, et al. The broad footprint of climate change from genes to biomes to people. Science. 2016;354:aaf7671. - PubMed
-
- Mizuno T, et al. Ambient Temperature Signal Feeds into the Circadian Clock Transcriptional Circuitry Through the EC Night-Time Repressor in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant & cell physiology. 2014;0:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Box MS, et al. ELF3 Controls Thermoresponsive Growth in Arabidopsis. Current Biology. 2014 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

