Loneliness and sleep: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32284871
- PMCID: PMC7139193
- DOI: 10.1177/2055102920913235
Loneliness and sleep: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Despite the mounting evidence linking loneliness with health, the mechanisms underlying this relationship remain obscure. This systematic review and meta-analysis on the association between loneliness and one potential mechanism-sleep-identified 27 relevant articles. Loneliness correlated with self-reported sleep disturbance (r = .28, 95% confidence interval (.24, .33)) but not duration, across a diverse set of samples and measures. There was no evidence supporting age or gender as moderators or suggesting publication bias. The longitudinal relationship between loneliness and sleep remains unclear. Loneliness is related to sleep disturbance, but research is necessary to determine directionality, examine the influence of other factors, and speak to causality.
Keywords: health; insomnia; loneliness; mechanisms; sleep.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
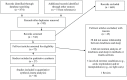


References
-
- Cacioppo JT, Hawkley LC, Bernston GC, et al. (2002. a) Do lonely days invade the nights? Potential social modulation of sleep efficiency. Psychological Science 13(4): 384–387. - PubMed
-
- Cacioppo JT, Hawkley LC, Crawford E, et al. (2002. b) Loneliness and health: Potential mechanisms. Psychosomatic Medicine 64(3): 407–417. - PubMed
-
- Christiansen J, Larsen FB, Lasgaard M. (2016) Do stress, health behavior, and sleep mediate the association between loneliness and adverse health conditions among older people? Social Science & Medicine 152: 80–86. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

