Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Opioids in Postsurgical Dental Pain
- PMID: 32286125
- PMCID: PMC7313348
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034520914254
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Opioids in Postsurgical Dental Pain
Abstract
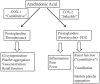
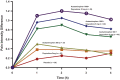
Postsurgical dental pain is mainly driven by inflammation, particularly through the generation of prostaglandins via the cyclooxygenase system. Thus, it is no surprise that numerous randomized placebo-controlled trials studying acute pain following the surgical extraction of impacted third molars have demonstrated the remarkable efficacy of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen sodium, etodolac, diclofenac, and ketorolac in this prototypic condition of acute inflammatory pain. Combining an optimal dose of an NSAID with an appropriate dose of acetaminophen appears to further enhance analgesic efficacy and potentially reduce the need for opioids. In addition to being on average inferior to NSAIDs as analgesics in postsurgical dental pain, opioids produce a higher incidence of side effects in dental outpatients, including dizziness, drowsiness, psychomotor impairment, nausea/vomiting, and constipation. Unused opioids are also subject to misuse and diversion, and they may cause addiction. Despite these risks, some dental surgical outpatients may benefit from a 1- or 2-d course of opioids added to their NSAID regimen. NSAID use may carry significant risks in certain patient populations, in which a short course of an acetaminophen/opioid combination may provide a more favorable benefit versus risk ratio than an NSAID regimen.
Keywords: acute pain; analgesics; inflammation; opioid abuse; prostaglandins; randomized controlled clinical trials.
Conflict of interest statement
Over the past 15 years, E.V. Hersh has received funding from Charleston Laboratories, Pfizer Consumer Healthcare, and AAI International and consulting fees from Johnson & Johnson and Bayer Pharmaceuticals. In the last 20 years P.A. Moore has served as a research consultant for several pharmaceutical companies, including Dentsply Pharmaceutical, Kodak Dental Systems, Septodont USA, St Renatus, Novalar Inc, and Novocol of Canada Inc. T. Grosser reports receiving consulting fees from Bayer Healthcare, Novartis, Plx Pharma and Aralez Pharmaceuticals and has received funding from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (HL117798). J.T. Farrar has received research grants and contracts from the US Food and Drug Administration and the NIH; consulting fees from Analgesic Solutions, Aptinyx, Biogen, Opioid Post-marketing Consortium, Daiichi Sankyo, DepoMed, Evadera, Jansen, Lilly, Novartis, Vertex, and Pfizer; and DSMB services from NIH-NIA and Cara Therapeutics. R.C. Polomano has received research grants and contracts from the NIH and an honorarium from AcelRx Pharmaceuticals for an educational program. M. Saraghi is the Dental Prescribing Practices Subject Matter Expert to the NYS Dept of Health, the latter is the recipient of a HRSA Grant to States to Support Oral Health Workforce Activities (T12HP30337). C.H. Mitchell is currently funded by the NIH (EY013434 and EY015537) and Astra Zeneca. S.A. Juska and K.N. Theken have no potential conflicts to report. The authors declare no further potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures



Comment in
-
Is the "Mission Accomplished" for the Management of Acute Oral Pain without Enabling Substance Abuse?J Dent Res. 2020 Jul;99(7):775-776. doi: 10.1177/0022034520916417. Epub 2020 Apr 14. J Dent Res. 2020. PMID: 32567991 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aronoff DM, Oates JA, Boutaud O. 2006. New insights into the mechanism of action of acetaminophen: its clinical pharmacologic characteristics reflect its inhibition of the two prostaglandin H2 synthases. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 79(1):9–19. - PubMed
-
- Bansal V, Dex T, Proskin H, Garreffa S. 2001. A look at the safety profile of over-the-counter naproxen sodium: a meta-analysis. J Clin Pharmacol. 41(2):127–138. - PubMed
-
- Barden J, Edwards JE, McQuay HJ, Wiffen PJ, Moore RA. 2004. Relative efficacy of oral analgesics after third molar extraction. Br Dent J. 97(7):407–411. - PubMed
-
- Benarroch EE. 2012. Endogenous opioid systems: current concepts and clinical correlations. Neurology. 79(8):807–814. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

