A Global View on Block Copolymers
- PMID: 32290129
- PMCID: PMC7240606
- DOI: 10.3390/polym12040869
A Global View on Block Copolymers
Abstract
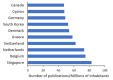
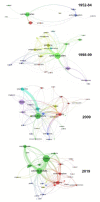
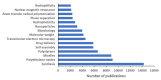
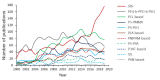
In this systematic review, a total of 45,143 publications on block copolymers, issued between 1952 and 2019, are analyzed in terms of number, source, language, institution, country, keywords, and block copolymer type, to find out their evolution and predict research trends. The number of publications devoted to block copolymers has been growing for over six decades, maintaining a consistent level throughout the last few years. In their majority, documents came out of the United States, although more recently, Chinese institutions are those displaying the largest production. Keywords analysis indicated that one-third of the publications concerned synthesis, around 20% explored self-assembly and morphological aspects, and another 20% referred to block copolymer applications in solution. In particular, 2019 confirmed the expansion of studies related to drug delivery, and in minor extent, to a deeper view of self-assembling. Styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer was the most popular in studies covering both basic and industrially oriented aspects. Other highly investigated copolymers are PEO-b-PPO-b-PEO (Pluronic©) and amphiphilic block copolymers based on polycaprolactone or poly(lactic acid), which owed their success to their potential as delivery vehicles. Future trending topics will concern nanomedicine challenges and technology-related applications, with a special attention toward the orientation and ordering of mesophase-separated morphologies.
Keywords: PS-b-PMMA; drug delivery; nanomaterials; poly(ethylene oxide); self-assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Hamley I.W. The Physics of Block Copolymers. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 1998.
-
- Fasolka M.J., Mayes A.M. Block Copolymer Thin Films: Physics and Applications. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2001;31:323–355. doi: 10.1146/annurev.matsci.31.1.323. - DOI
-
- Rodríguez-Hernández J., Chécot F., Gnanou Y., Lecommandoux S. Toward ‘Smart’ Nano-objects by Self-assembly of Block Copolymers in Solution. Progr. Polym. Sci. 2005;30:691–724. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2005.04.002. - DOI
-
- Schmidt B.V.K.J. Double Hydrophilic Block Copolymer Self-Assembly in Aqueous Solution. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2018;219:1700494. doi: 10.1002/macp.201700494. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

