Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters: United We Stand Divided We Fall
- PMID: 32290245
- PMCID: PMC7177734
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21072653
Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters: United We Stand Divided We Fall
Abstract
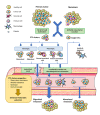
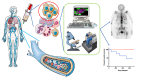
The presence of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and CTC clusters, also known as tumor microemboli, in biological fluids has long been described. Intensive research on single CTCs has made a significant contribution in understanding tumor invasion, metastasis tropism, and intra-tumor heterogeneity. Moreover, their being minimally invasive biomarkers has positioned them for diagnosis, prognosis, and recurrence monitoring tools. Initially, CTC clusters were out of focus, but major recent advances in the knowledge of their biogenesis and dissemination reposition them as critical actors in the pathophysiology of cancer, especially metastasis. Increasing evidence suggests that "united" CTCs, organized in clusters, resist better and carry stronger metastatic capacities than "divided" single CTCs. This review gathers recent insight on CTC cluster origin and dissemination. We will focus on their distinct molecular package necessary to resist multiple cell deaths that all circulating cells normally face. We will describe the molecular basis of their increased metastatic potential as compared to single CTCs. We will consider their clinical relevance as prognostic biomarkers. Finally, we will propose future directions for research and clinical applications in this promising topic in cancer.
Keywords: CTC; circulating tumor cells; circulating tumor cells clusters; liquid biopsy; microemboli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Beerling E., Seinstra D., de Wit E., Kester L., van der Velden D., Maynard C., Schäfer R., van Diest P., Voest E., van Oudenaarden A., et al. Plasticity between Epithelial and Mesenchymal States Unlinks EMT from Metastasis-Enhancing Stem Cell Capacity. Cell Rep. 2016;14:2281–2288. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.02.034. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

