A Durable Hybrid RAM Disk with a Rapid Resilience for Sustainable IoT Devices
- PMID: 32290359
- PMCID: PMC7218718
- DOI: 10.3390/s20082159
A Durable Hybrid RAM Disk with a Rapid Resilience for Sustainable IoT Devices
Abstract
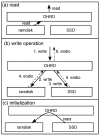
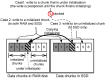
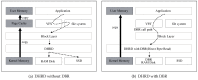
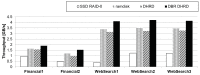
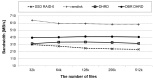
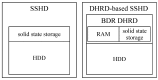
Flash-based storage is considered to be a de facto storage module for sustainable Internet of things (IoT) platforms under a harsh environment due to its relatively fast speed and operational stability compared to disk storage. Although their performance is considerably faster than disk-based mechanical storage devices, the read and write latency still could not catch up with that of Random-access memory (RAM). Therefore, RAM could be used as storage devices or systems for time-critical IoT applications. Despite such advantages of RAM, a RAM-based storage system has limitations in its use for sustainable IoT devices due to its nature of volatile storage. As a remedy to this problem, this paper presents a durable hybrid RAM disk enhanced with a new read interface. The proposed durable hybrid RAM disk is designed for sustainable IoT devices that require not only high read/write performance but also data durability. It includes two performance improvement schemes: rapid resilience with a fast initialization and direct byte read (DBR). The rapid resilience with a fast initialization shortens the long booting time required to initialize the durable hybrid RAM disk. The new read interface, DBR, enables the durable hybrid RAM disk to bypass the disk cache, which is an overhead in RAM-based storages. DBR performs byte-range I/O, whereas direct I/O requires block-range I/O; therefore, it provides a more efficient interface than direct I/O. The presented schemes and device were implemented in the Linux kernel. Experimental evaluations were performed using various benchmarks at the block level till the file level. In workloads where reads and writes were mixed, the durable hybrid RAM disk showed 15 times better performance than that of Solid-state drive (SSD) itself.
Keywords: IoT; direct byte read; hybrid RAM disk; operating system; secondary storage; sustainability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Bagatin M., Gerardin S., Paccagnella A., Beltrami S., Camerlenghi E., Bertuccio M., Costantino A., Zadeh A., Ferlet-Cavrois V., Santin G., et al. Effects of heavy-ion irradiation on vertical 3-D NAND flash memories. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2017;65:318–325. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2017.2777887. - DOI
-
- Fedorchenko A., Kotenko I.V., Chechulin A. Integrated Repository of Security Information for Network Security Evaluation. JoWUA. 2015;6:41–57.
-
- Android Things. [(accessed on 10 April 2020)]; Available online: https://developer.android.com/things.
-
- Ninglekhu J., Krishnan R., John E., Panday M. Securing Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators Using Smartphones. J. Internet Serv. Inf. Secur. (JISIS) 2015;5:47–64.
-
- Jo H., Kang J.U., Park S.Y., Kim J.S., Lee J. FAB: Flash-aware buffer management policy for portable media players. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2006;52:485–493.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

