Human Wharton's Jelly-Cellular Specificity, Stemness Potency, Animal Models, and Current Application in Human Clinical Trials
- PMID: 32290584
- PMCID: PMC7230974
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9041102
Human Wharton's Jelly-Cellular Specificity, Stemness Potency, Animal Models, and Current Application in Human Clinical Trials
Abstract
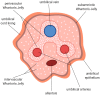
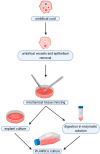
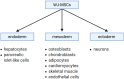
Stem cell therapies offer a great promise for regenerative and reconstructive medicine, due to their self-renewal and differentiation capacity. Although embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, their utilization involves embryo destruction and is ethically controversial. Therefore, adult tissues that have emerged as an alternative source of stem cells and perinatal tissues, such as the umbilical cord, appear to be particularly attractive. Wharton's jelly, a gelatinous connective tissue contained in the umbilical cord, is abundant in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) that express CD105, CD73, CD90, Oct-4, Sox-2, and Nanog among others, and have the ability to differentiate into osteogenic, adipogenic, chondrogenic, and other lineages. Moreover, Wharton's jelly-derived MSCs (WJ-MSCs) do not express MHC-II and exhibit immunomodulatory properties, which makes them a good alternative for allogeneic and xenogeneic transplantations in cellular therapies. Therefore, umbilical cord, especially Wharton's jelly, is a promising source of mesenchymal stem cells.
Keywords: Wharton’s jelly; stem cells; umbilical cord.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Doğan A. Embryonic stem cells in development and regenerative medicine. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018;1079:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Gruber H.E., Deepe R., Hoelscher G.L., Ingram J.A., Norton H.J., Scannell B., Loeffler B.J., Zinchenko N., Hanley E.N., Tapp H. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Direction to a phenotype sharing similarities with the disc, gene expression profiling, and coculture with human annulus cells. Tissue Eng. Part A. 2010;16:2843–2860. doi: 10.1089/ten.tea.2009.0709. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

