Why tocilizumab could be an effective treatment for severe COVID-19?
- PMID: 32290839
- PMCID: PMC7154566
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-020-02339-3
Why tocilizumab could be an effective treatment for severe COVID-19?
Abstract
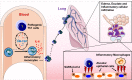
A severe pneumonia-associated respiratory syndrome caused by a new coronavirus was identified in December 2019 (COVID-19), spread rapidly and has become a world-wide public health challenge. About 25% of COVID-19 patients experienced severe complications including acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and even progressed into an intensive care unit (ICU) admission and died. The exploration for the mortality causes and advancing novel therapeutic development of severe COVID-19 is crucial at the moment. The biopsy samples analysis at autopsy suggested that increased alveolar exudate caused by aberrant host immune response and inflammatory cytokine storm probably impedes alveolar gas exchange and contributes to the high mortality of severe COVID-19 patients. Our research has identified that pathogenic T cells and inflammatory monocytes incite inflammatory storm with large amount of interleukin 6, therefore monoclonal antibody that targets the IL-6 pathways may potentially curb inflammatory storm. Moreover, Tocilizumab treatment that blocking IL-6 receptors showed inspiring clinical results including temperature returned to normal quickly and respiratory function improved. Therefore, we suggest that Tocilizumab is an effective treatment in severe patients of COVID-19 to calm the inflammatory storm and reduce mortality.
Keywords: Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS); COVID-19; IL-6; Inflammatory storm; SARS-CoV-2; Tocilizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Anti-IL6R role in treatment of COVID-19-related ARDS.J Transl Med. 2020 Apr 14;18(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02333-9. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32290847 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Utilizing tocilizumab for the treatment of cytokine release syndrome in COVID-19.J Clin Virol. 2020 Jul;128:104443. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104443. Epub 2020 May 16. J Clin Virol. 2020. PMID: 32425661 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2020YFC0843800/the China National Center for Biotechnology Development 182/International
- 81788101/the Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81922028/the Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 2019442/Youth Innovation Promotion Association of Chinese Academy of Sciences/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous