Combining bioinformatics and biological detection to identify novel biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of pulmonary tuberculosis
- PMID: 32291421
- PMCID: PMC7841615
- DOI: 10.15537/smj.2020.4.24989
Combining bioinformatics and biological detection to identify novel biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of pulmonary tuberculosis
Abstract
Objectives: To identify the novel and promising indicators for pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) patients.
Methods: The study was carried out between June 2016 and June 2019. Three RNA sequencing or microarray datasets of TB infection were used to identify the potential genes showing a common expression trend. The expression level of screened targets was determined by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and ELISA using samples of whole blood and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) isolated from 69 PTB patients and 69 healthy volunteers. The potential of the identified targets to predict the treatment outcomes was further studied.
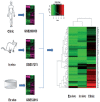
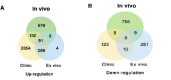
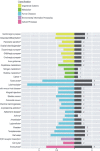
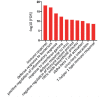
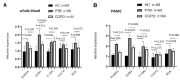
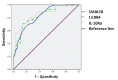
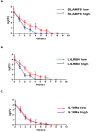
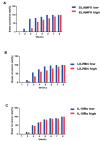
Results: Bioinformatics analysis demonstrated that a total of 91 genes were up-regulated in all the 3 datasets; among them, the expression of SLAMF8, LILRB4, and IL-10Ra was significantly increased at both the mRNA and protein levels in whole blood and PBMC samples of PTB patients compared with the healthy controls. The mortality rate increased significantly in SLAMF8 or LILRB4 high expression group compared with SLAMF8 or LILRB4 low expression group. Further, the decrease rate of bacteria in patients with SLAMF8 or LILRB4 high expression was slower than that in patients with SLAMF8 or LILRB4 low expression.
Conclusion: This study provides a promising way to identify novel indicators for PTB. Moreover, the LILRB4 expression may play a role in predicting the outcome of treatments on PTB patients.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Discovery and verification of serum differential expression proteins for pulmonary tuberculosis.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2015 Sep;95(5):547-54. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2015. PMID: 26276261
-
Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis via identification of core genes and pathways utilizing blood transcriptional signatures: a multicohort analysis.Respir Res. 2022 May 14;23(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02035-4. Respir Res. 2022. PMID: 35568895 Free PMC article.
-
The Peripheral Blood Transcriptome Is Correlated With PET Measures of Lung Inflammation During Successful Tuberculosis Treatment.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 10;11:596173. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.596173. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33643286 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of pathologic inflammation by leukocyte Ig-like receptor B4 and related inhibitory receptors.Immunol Rev. 2007 Jun;217:222-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2007.00522.x. Immunol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17498062 Review.
-
LILRB4 as a novel immunotherapeutic target for multiple diseases.Biochem Pharmacol. 2025 Mar;233:116762. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2025.116762. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Biochem Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39842553 Review.
Cited by
-
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B4: A keystone in immune modulation and therapeutic target in cancer and beyond.Cancer Innov. 2024 Oct 22;3(6):e153. doi: 10.1002/cai2.153. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cancer Innov. 2024. PMID: 39444949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers That Correlate with Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis Treatment Response: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Clin Microbiol. 2022 Feb 16;60(2):e0185921. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01859-21. Epub 2021 Dec 15. J Clin Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34911364 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Validation of Novel Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Liver Fibrosis/Cirrhosis and Chronic Hepatitis B via Transcriptome Sequencing Technology.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022 May 9;9:389-403. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S357380. eCollection 2022. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022. PMID: 35592243 Free PMC article.
-
LILRB4, from the immune system to the disease target.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Jul 15;12(7):3149-3166. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32774691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B: therapeutic targets in cancer.Antib Ther. 2021 Feb 9;4(1):16-33. doi: 10.1093/abt/tbab002. eCollection 2021 Jan. Antib Ther. 2021. PMID: 33928233 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schluger NW. AJRCCM:100-Year Anniversary. Focus on Tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195:1112–1114. - PubMed
-
- Furin J, Cox H, Pai M. Tuberculosis. Lancet. 2019;393:1642–1656. - PubMed
-
- Bloom CI, Graham CM, Berry MP, Rozakeas F, Redford PS, Wang Y, et al. The circular RNA of peripheral blood mononuclear cells:Hsa_circ_0005836 as a new diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target of active pulmonary tuberculosis. Mol Immunol. 2017;90:264–272. - PubMed
-
- Walzl G, McNerney R, du Plessis N, Bates M, McHugh TD, Chegou NN, et al. Tuberculosis:advances and challenges in development of new diagnostics and biomarkers. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18:e199–e210. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

