Successful Treatment of a Massive Desmoplastic Fibroma of the Ilium without Surgery: A Case Report with Long-Term Follow-Up
- PMID: 32292618
- PMCID: PMC7148584
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/5380598
Successful Treatment of a Massive Desmoplastic Fibroma of the Ilium without Surgery: A Case Report with Long-Term Follow-Up
Abstract
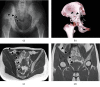
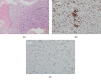
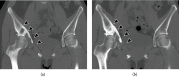
Desmoplastic fibroma of the bone (DFB) is a notably rare, lytic, locally aggressive but nonmetastatic, primary benign bone tumor in patients less than 30 years old. As the recommended primary treatment for DFB, wide resection is preferred to curettage from the perspective of recurrence but wide resection of DFB in the pelvis such as in the acetabulum could result in greater functional loss, suggesting the need for conservative treatments. However, there is no report on long-term follow-up following conservative treatment for DFB. The present case involved a 21-year-old woman with right hip pain. Radiological evaluation revealed a massive lesion throughout the right ilium and acetabulum with partial osteolysis, cortical destruction, marginal sclerosis, slight pseudotrabeculation, and bone expansion. Open biopsy from the ilium showed the proliferation of spindle cells in an abundant collagenous matrix without atypia and mitosis, suggesting a diagnosis of DFB. Conservative treatment was selected considering the risk of greater functional loss following wide ilium resection. An evaluation 10 years after follow-up showed a partially sclerotic lesion of the ilium and the absence of pain. The current case demonstrates that conservative therapy may be effective even in some cases of aggressive DFB.
Copyright © 2020 Hideyuki Kinoshita et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest directly relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Smith S. E., Kransdorf M. J. Primary musculoskeletal tumors of fibrous origin. Seminars in Musculoskeletal Radiology. 2000;4(1):73–88. - PubMed
-
- Jaffe H. Tumors and Tumorous Conditions of the Bones and Joints. Philadelphia, PA, USA: Lea & Feibiger; 1958.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

