Safety management of nasopharyngeal specimen collection from suspected cases of coronavirus disease 2019
- PMID: 32292635
- PMCID: PMC7129371
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnss.2020.03.012
Safety management of nasopharyngeal specimen collection from suspected cases of coronavirus disease 2019
Abstract
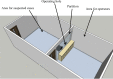
This article introduces safety management strategies of nasopharyngeal specimen collection from suspected cases of coronavirus disease 2019 in a tertiary designated hospital. The key points include establishing a special sampling room, strict sterilization of the entire environment, training of professional nurses, enhancement of personal protection, standardization of methods and processes for swab collection, and a timely and safety sample submission. More than 11,000 nasopharyngeal specimens were collected by eight nurses, with an average of 1,375 specimen swab collections each nurse, and no one was infected.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019; Nasopharyngeal swabs; Safety management; Specimen collection.
© 2020 Chinese Nursing Association. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine [Internet] The national health commission of the People’s Republic of China: corona virus disease 2019 diagnosis and treatment plan (5th trial edition revised version) 2020-02-08. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-02/09/5476407/files/765d1e65b7d... [cited 2020 Feb 17]. Available from:
-
- WHO [Internet] 2020-02-07. Infection prevention and control during health care when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected.https://www.who.int/publications-detail/infection-prevention-and-control... [cited 2020 Feb 17]. Available from:
-
- Emergency General Hospital [Internet] 2020-01-28. Manual for prevention and control of novel coronavirus Pneumonia.http://www.xinhuanet.com/politics/2020-01/28/c_1125508409.htm [cited 2020 Feb 17]. Available from:
-
- Yao X., Zhang B.L., Gong Y.X., Zhang Y., Lu Q., Yang H. Investigation on implementing the hospital air purification management standard WS/T368-2012. Chin J Infect Control. 2019;18(11):1032–1037.
-
- WHO Global guidelines on the prevention of surgical site infection. https://www.who.int/gpsc/ssi-guidelines/en/ [cited 2020 Feb 17]. Available from:
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical