Key role of macrophages in tolerance induction via T regulatory type 1 (Tr1) cells
- PMID: 32293025
- PMCID: PMC7366746
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13440
Key role of macrophages in tolerance induction via T regulatory type 1 (Tr1) cells
Abstract
T regulatory type 1 (Tr1) cells are a class of regulatory T cells (Tregs ) participating in peripheral tolerance, hence the rationale behind their testing in clinical trials in different disease settings. One of their applications is tolerance induction to allogeneic islets for long-term diabetes-free survival. Currently the cellular and molecular mechanisms that promote Tr1-cell induction in vivo remain poorly understood. We employed a mouse model of transplant tolerance where treatment with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)/rapamycin induces permanent engraftment of allogeneic pancreatic islets in C57BL/6 mice via Tr1 cells. The innate composition of graft and spleen cells in tolerant mice was analyzed by flow cytometry. Graft phagocytic cells were co-cultured with CD4+ T cells in vitro to test their ability to induce Tr1-cell induction. Graft phagocytic cells were depleted in vivo at different time-points during G-CSF/rapamycin treatment, to identify their role in Tr1-cell induction and consequently in graft survival. In the spleen, the site of Tr1-cell induction, no differences in the frequencies of macrophages or dendritic cells (DC) were observed. In the graft, the site of antigen uptake, a high proportion of macrophages and not DC was detected in tolerant but not in rejecting mice. Graft-infiltrating macrophages of G-CSF/rapamycin-treated mice had an M2 phenotype, characterized by higher CD206 expression and interleukin (IL)-10 production, whereas splenic macrophages only had an increased CD206 expression. Graft-infiltrating cells from G-CSF/rapamycin-treated mice-induced Tr1-cell expansion in vitro. Furthermore, Tr1-cell induction was perturbed upon in-vivo depletion of phagocytic cells, early and not late during treatment, leading to graft loss suggesting that macrophages play a key role in tolerance induction mediated by Tr1 cells. Taken together, in this mouse model of Tr1-cell induced tolerance to allogeneic islets, M2 macrophages infiltrating the graft upon G-CSF/rapamycin treatment are key for Tr1-cell induction. This work provides mechanistic insight into pharmacologically induced Tr1-cell expansion in vivo in this stringent model of allogeneic transplantation.
Keywords: macrophage; regulatory T cells; tolerance; transplantation.
© 2020 British Society for Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial and commercial conflicts of interest.
Figures
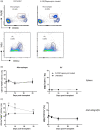

 ) or with clodronate liposome treatment at day 0 (
) or with clodronate liposome treatment at day 0 ( ), day 14 (
), day 14 ( ), day 21 (
), day 21 ( ) and day 30 (
) and day 30 ( ); n = 4–6/group.
); n = 4–6/group.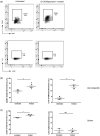


References
-
- Sanda S, Roep BO, von Herrath M. Islet antigen specific IL‐10+ immune responses but not CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ cells at diagnosis predict glycemic control in type 1 diabetes. Clin Immunol 2008; 127:138–43. - PubMed
-
- Roncarolo MG, Gregori S, Bacchetta R, Battaglia M, Gagliani N. The biology of T regulatory type 1 cells and their therapeutic application in immune‐mediated diseases. Immunity 2018; 49:1004–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

