Treatment with convalescent plasma for COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, China
- PMID: 32293713
- PMCID: PMC7262027
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.25882
Treatment with convalescent plasma for COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, China
Abstract
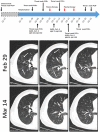
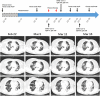
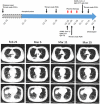
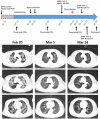
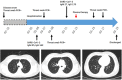
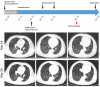
The discovery of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are causing public health emergencies. A handful pieces of literature have summarized its clinical and radiologic features, whereas therapies for COVID-19 are rather limited. To evaluate the efficacy of convalescent plasma therapy in COVID-19 patients, we did this timely descriptive study. Six laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patients were enrolled and received the transfusion of ABO-compatible convalescent plasma. The efficacy of this intervention was determined by the alleviation of symptoms, changes in radiologic abnormalities and laboratory tests. No obvious adverse effect observed during the treatment. Transfusion of convalescent plasma led to a resolution of ground-glass opacities and consolidation in patients #1, #2, #3, #4, and #6. In patients #1 and #5 who presented with SARS-CoV-2 in throat swab, convalescent plasma therapy elicited an elimination of the virus. Serologic analysis indicated an immediate increase in anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers in patients #2 and #3, but not in patient #1. This study indicates that convalescent plasma therapy is effective and specific for COVID-19. This intervention has a special significance for eliminating SARS-CoV-2 and is believed to be a promising state-of-the-art therapy during COVID-19 pandemic crisis.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; convalescent plasma therapy.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gillespie TR, Leendertz FH. COVID‐19: protect great apes during human pandemics. Nature. 2020;579(7800):497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

