Microvascular COVID-19 lung vessels obstructive thromboinflammatory syndrome (MicroCLOTS): an atypical acute respiratory distress syndrome working hypothesis
- PMID: 32294809
- PMCID: PMC10692450
- DOI: 10.51893/2020.2.pov2
Microvascular COVID-19 lung vessels obstructive thromboinflammatory syndrome (MicroCLOTS): an atypical acute respiratory distress syndrome working hypothesis
Abstract
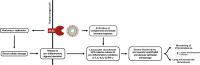
We suggest the use of MicroCLOTS (microvascular COVID-19 lung vessels obstructive thromboinflammatory syndrome) as a new name for severe pulmonary coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We hypothesise that, in predisposed individuals, alveolar viral damage is followed by an inflammatory reaction and by microvascular pulmonary thrombosis. This progressive endothelial thromboinflammatory syndrome may also involve the microvascular bed of the brain and other vital organs, leading to multiple organ failure and death. Future steps in the understanding of the disease and in the identification of treatments may benefit from this definition and hypothesised sequence of events.
Keywords: COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Comment in
-
A rationale for blocking thromboinflammation in COVID-19 with Btk inhibitors.Platelets. 2020 Jul 3;31(5):685-690. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2020.1775189. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Platelets. 2020. PMID: 32552307 No abstract available.
-
Microvascular COVID-19 lung vessels obstructive thromboinflammatory syndrome (MicroCLOTS): a new variant of thrombotic microangiopathy?Crit Care Resusc. 2020 Sep;22(3):284. doi: 10.1016/S1441-2772(23)00399-X. Crit Care Resusc. 2020. PMID: 32900338 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when COVID-19 is suspected. Interim guidance. Version 1.2. 13 March 2020 https://www.who.int/publications-detail/clinical-management-of-severe-ac... (viewed Apr 2020)
-
- Herold T., Jurinovic V., Arnreich C., et al. Level of IL-6 predicts respiratory failure in hospitalized symptomatic COVID-19 patients. BMJ. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.04.01.20047381. [Preprint, 10 April 2020] - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical