Recent Advances in Manufacturing Innovative Stents
- PMID: 32294908
- PMCID: PMC7238261
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12040349
Recent Advances in Manufacturing Innovative Stents
Abstract
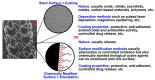
Cardiovascular diseases are the most distributed cause of death worldwide. Stenting of arteries as a percutaneous transluminal angioplasty procedure became a promising minimally invasive therapy based on re-opening narrowed arteries by stent insertion. In order to improve and optimize this method, many research groups are focusing on designing new or improving existent stents. Since the beginning of the stent development in 1986, starting with bare-metal stents (BMS), these devices have been continuously enhanced by applying new materials, developing stent coatings based on inorganic and organic compounds including drugs, nanoparticles or biological components such as genes and cells, as well as adapting stent designs with different fabrication technologies. Drug eluting stents (DES) have been developed to overcome the main shortcomings of BMS or coated stents. Coatings are mainly applied to control biocompatibility, degradation rate, protein adsorption, and allow adequate endothelialization in order to ensure better clinical outcome of BMS, reducing restenosis and thrombosis. As coating materials (i) organic polymers: polyurethanes, poly(ε-caprolactone), styrene-b-isobutylene-b-styrene, polyhydroxybutyrates, poly(lactide-co-glycolide), and phosphoryl choline; (ii) biological components: vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and anti-CD34 antibody and (iii) inorganic coatings: noble metals, wide class of oxides, nitrides, silicide and carbide, hydroxyapatite, diamond-like carbon, and others are used. DES were developed to reduce the tissue hyperplasia and in-stent restenosis utilizing antiproliferative substances like paclitaxel, limus (siro-, zotaro-, evero-, bio-, amphi-, tacro-limus), ABT-578, tyrphostin AGL-2043, genes, etc. The innovative solutions aim at overcoming the main limitations of the stent technology, such as in-stent restenosis and stent thrombosis, while maintaining the prime requirements on biocompatibility, biodegradability, and mechanical behavior. This paper provides an overview of the existing stent types, their functionality, materials, and manufacturing conditions demonstrating the still huge potential for the development of promising stent solutions.
Keywords: bioresorbable stent stent manufacturing; drug-eluting stent; stent; stent coating; titanium oxynitride coating.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Wu T., McCarthy S. In: Coronary Arterial Drug-Eluting Stent: From Structure to Clinical Coronary Artery Diseases. Chaikovsky I., editor. InTech; Rijeka, Croatia: 2012. pp. 197–224.
-
- Zhu Y.Q., Yang K., Cheng R.Y., Xiang Y., Yuan T.W., Sarmento B.N., Chen Y.S., Cui W.G. The current status of biodegradable stent to treat benign luminal disease. Mater. Today. 2017;20:516–529.
-
- Khan W., Farah S., Domb A.J. Drug eluting stents: Developments and current status. J. Control. Release. 2012;161:703–712. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

