Get the message? A scoping review of physical activity messaging
- PMID: 32295613
- PMCID: PMC7160981
- DOI: 10.1186/s12966-020-00954-3
Get the message? A scoping review of physical activity messaging
Abstract
Background: Understanding how to create and deliver effective physical activity (PA) messages for and to various population subgroups may play a role in increasing population PA levels. This scoping review aimed to provide an overview of what is known about PA messaging and highlight key research gaps.
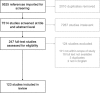
Methods: We followed a 5-stage protocol proposed by Arksey & O'Malley and the Preferred Reporting Items For Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) extension for scoping reviews checklist. Stage 1: research questions were identified. Stage 2: we identified relevant studies by searching electronic databases, contacting existing networks and hand searching reference lists. Stage 3: studies were screened in Covidence™ software. Stage 4: study data were extracted and charted. Stage 5: findings from included studies were collated, summarised and reported in two ways: (1) a descriptive numerical analysis providing insight into extent, nature and distribution of the included studies, and (2) a narrative summary summarizing the evidence reviewed organised by messaging concepts and by population subgroup.
Results: A total of 9525 references were imported into Covidence™ for screening. Of these, 123 studies were included in final analysis. We found that PA messaging evidence is complex and multidimensional in nature, with numerous concepts to consider when creating or evaluating messages. The extent to which these different PA messaging concepts have been researched is variable. Where research has accumulated and evidence is consistent, it supports the following: (1) PA messages should be framed positively and highlight short-term outcomes specifically relating to social and mental health, (2) message content should be tailored or targeted to intended recipient(s), and (3) when developing messages, formative research, psychological theory and/or social marketing principles should be used.
Conclusion: While it is unlikely to address global inactivity on its own, PA messaging may play a valuable role improving population PA levels. However, it is a complex and multidimensional concept and greater understanding is still needed. We present a synthesis of the existing evidence, highlighting key areas where evidence has accumulated and where gaps lie, as well as recommendations for PA messaging to different population subgroups.
Keywords: Communication; Dissemination; Exercise; Guidelines; Public health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical