EUS-guided biliary drainage: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32295967
- PMCID: PMC7279084
- DOI: 10.4103/eus.eus_80_19
EUS-guided biliary drainage: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
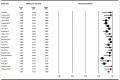
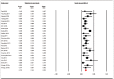
ERCP is the current procedure of choice for patients with jaundice caused by biliary obstruction. EUS-guided biliary drainage (EUS-BD) has emerged as an alternative to ERCP in patients requiring biliary drainage. The aim of the study was to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis to report the overall efficacy and safety of EUS-BD. We conducted a comprehensive search of several databases including PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, Google Scholar, and LILACS databases (earliest inception to June 2018) to identify studies that reported EUS-BD in patients. The primary outcome was to look at the technical and clinical success of the procedure. The secondary analysis focused on calculating the pooled rate of re-interventions and all adverse-events, along with the commonly reported adverse-event subtypes. Twenty-three studies reporting on 1437 patients were identified undergoing 1444 procedures. Majority of the patient population were male (53.86%), with an average age of 67.22 years. The pooled technical success rates and clinical success rates were 91.5% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 87.7-94.2, I[2] = 76.5) and 87% (95% CI: 82.3-90.6, I[2] = 72.4), respectively. The total adverse event rates were 17.9% (95% CI: 14.3-22.2, I[2] = 69.1). Subgroup analysis of three major individual adverse events was bile leak: 4.1% (2.7-6.2, I[2] = 46.7), stent migration: 3.9% (2.5-6.2, I[2] = 43.5), and infection: 3.8% (2.8-5.1, I[2] = 0) Substantial heterogeneity was noted in the analysis. EUS-BD has high technical and clinical success rate and hence a very effective procedure. Concerns about publication bias exist. Careful consideration should be given to the adverse events and weighing the risks and benefits of the alternative nonsurgical/surgical approaches.
Keywords: Biliary drainage; Biliary obstruction; ERCP; EUS guided; jaundice.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Enochsson L, Swahn F, Arnelo U, et al. Nationwide, population-based data from 11,074 ERCP procedures from the Swedish registry for gallstone surgery and ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72:1175–84. 1184e1-3. - PubMed
-
- Giovannini M, Moutardier V, Pesenti C, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided bilioduodenal anastomosis: A new technique for biliary drainage. Endoscopy. 2001;33:898–900. - PubMed
-
- Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25:603–5. - PubMed
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–88. - PubMed
-
- Sutton AJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR, et al. Methods for Meta-Analysis in Medical Research. New York: John Wiley and Sons Ltd; 2000. pp. 205–8.