LRP1 is a master regulator of tau uptake and spread
- PMID: 32296178
- PMCID: PMC7687380
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2156-5
LRP1 is a master regulator of tau uptake and spread
Abstract
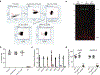
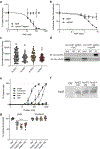
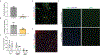
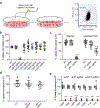
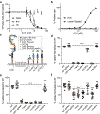
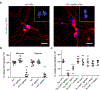
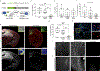
The spread of protein aggregates during disease progression is a common theme underlying many neurodegenerative diseases. The microtubule-associated protein tau has a central role in the pathogenesis of several forms of dementia known as tauopathies-including Alzheimer's disease, frontotemporal dementia and chronic traumatic encephalopathy1. Progression of these diseases is characterized by the sequential spread and deposition of protein aggregates in a predictable pattern that correlates with clinical severity2. This observation and complementary experimental studies3,4 have suggested that tau can spread in a prion-like manner, by passing to naive cells in which it templates misfolding and aggregation. However, although the propagation of tau has been extensively studied, the underlying cellular mechanisms remain poorly understood. Here we show that the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1) controls the endocytosis of tau and its subsequent spread. Knockdown of LRP1 significantly reduced tau uptake in H4 neuroglioma cells and in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons. The interaction between tau and LRP1 is mediated by lysine residues in the microtubule-binding repeat region of tau. Furthermore, downregulation of LRP1 in an in vivo mouse model of tau spread was found to effectively reduce the propagation of tau between neurons. Our results identify LRP1 as a key regulator of tau spread in the brain, and therefore a potential target for the treatment of diseases that involve tau spread and aggregation.
Figures
Comment in
-
A receptor that lets dementia-associated tau proteins into neurons.Nature. 2020 Apr;580(7803):326-327. doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-00874-z. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32238893 No abstract available.
-
Mechanistic insight into the spread of tau pathology.Nat Rev Neurol. 2020 Jun;16(6):298. doi: 10.1038/s41582-020-0360-4. Nat Rev Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32300227 No abstract available.
-
LRP1: A Novel Mediator of Tau Uptake.Mov Disord. 2020 Jul;35(7):1136. doi: 10.1002/mds.28107. Epub 2020 May 23. Mov Disord. 2020. PMID: 32445197 No abstract available.
-
Commentary: LRP1 Is a Master Regulator of Tau Uptake and Spread.Front Neurol. 2020 Dec 23;11:557509. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.557509. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33424736 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Additional References
-
- Obermoeller-McCormick LM et al. Dissection of receptor folding and ligand-binding property with functional minireceptors of LDL receptor-related protein. J Cell Sci 114, 899–908 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Usenovic M et al. Internalized Tau Oligomers Cause Neurodegeneration by Inducing Accumulation of Pathogenic Tau in Human Neurons Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 35, 14234–14250, doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1523-15.2015 (2015). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

