Management of multiligament knee injuries
- PMID: 32296548
- PMCID: PMC7144894
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.190012
Management of multiligament knee injuries
Abstract
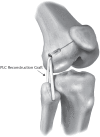
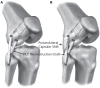
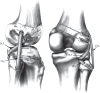
Up to 18% of multiligament knee injuries (MLKI) have an associated vascular injury.All MLKI should be assessed using the ankle brachial pressure index (ABPI) with selective arteriography if ABPI is < 0.9.An ischaemic limb following knee dislocation must be taken to the operating theatre immediately for stabilization and re-vascularization.Partial common peroneal nerve (CPN) injury following MLKI has better recovery than complete palsy.Posterior tibial tendon transfer is offered to patients with complete CPN palsy if there is no recovery at six months.Operative treatment with acute or staged reconstructions provides the best outcome in MLKI.Effective repair can only be performed within three weeks of injury.There is no difference between repair and reconstruction of medial collateral ligament and posteromedial corner.Posterolateral corner reconstruction has a lower failure rate than repair.Early mobilization following MLKI surgery results in fewer range-of-motion deficits. Cite this article: EFORT Open Rev 2020;5:145-155. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.190012.
Keywords: knee dislocation; multiligament knee injuries.
© 2020 The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
ICMJE Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest relevant to this work.
Figures



References
-
- Ng JWG, Price K, Deepak S. Knee pain in children. Paediatr Child Health 2019;29:521–527.
-
- Schenck RC. Classification of knee dislocations. In: Fanelli GC, ed. The multiple ligament injured knee: a practical guide to management. New York, NY: Springer, 2004:37–49.
-
- Howells NR, Brunton LR, Robinson J, Porteus AJ, Eldridge JD, Murray JR. Acute knee dislocation: an evidence based approach to the management of the multiligament injured knee. Injury 2011;42:1198–1204. - PubMed
-
- Peskun CJ, Whelan DB. Outcomes of operative and nonoperative treatment of multiligament knee injuries: an evidence-based review. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev 2011;19:167–173. - PubMed
-
- Dedmond BT, Almekinders LC. Operative versus nonoperative treatment of knee dislocations: a meta-analysis. Am J Knee Surg 2001;14:33–38. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

