Applied machine learning and artificial intelligence in rheumatology
- PMID: 32296743
- PMCID: PMC7151725
- DOI: 10.1093/rap/rkaa005
Applied machine learning and artificial intelligence in rheumatology
Abstract
Machine learning as a field of artificial intelligence is increasingly applied in medicine to assist patients and physicians. Growing datasets provide a sound basis with which to apply machine learning methods that learn from previous experiences. This review explains the basics of machine learning and its subfields of supervised learning, unsupervised learning, reinforcement learning and deep learning. We provide an overview of current machine learning applications in rheumatology, mainly supervised learning methods for e-diagnosis, disease detection and medical image analysis. In the future, machine learning will be likely to assist rheumatologists in predicting the course of the disease and identifying important disease factors. Even more interestingly, machine learning will probably be able to make treatment propositions and estimate their expected benefit (e.g. by reinforcement learning). Thus, in future, shared decision-making will not only include the patient's opinion and the rheumatologist's empirical and evidence-based experience, but it will also be influenced by machine-learned evidence.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; deep learning; machine learning; neural networks; rheumatology.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures



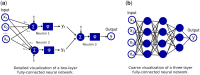
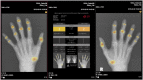
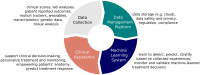
References
-
- Breiman L. Statistical modeling: the two cultures (with comments and a rejoinder by the author). Stat Sci 2001;16:199–231.
-
- LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G.. Deep learning. Nature 2015;521:436–44. - PubMed
-
- Hirschberg J, Manning CD.. Advances in natural language processing. Science 2015;349:261–6. - PubMed
-
- Devlin J, Chang M-W, Lee K, Toutanova K. BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. ArXiv181004805 Cs NAACL-HLT (2019).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
