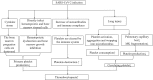
Mechanism of thrombocytopenia in COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 32296910
- PMCID: PMC7156897
- DOI: 10.1007/s00277-020-04019-0
Mechanism of thrombocytopenia in COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Since December 2019, a novel coronavirus has spread throughout China and across the world, causing a continuous increase in confirmed cases within a short period of time. Some studies reported cases of thrombocytopenia, but hardly any studies mentioned how the virus causes thrombocytopenia. We propose several mechanisms by which coronavirus disease 2019 causes thrombocytopenia to better understand this disease and provide more clinical treatment options.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019; Platelet; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; Thrombocytopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Thrombocytopenia in COVID-19: pathophysiology matters.Ann Hematol. 2021 Aug;100(8):2139-2140. doi: 10.1007/s00277-020-04183-3. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Ann Hematol. 2021. PMID: 32683455 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Chen Z, Zhang W, Lu Y, Guo C, Guo Z, Liao C et al (2020) From SARS-CoV to Wuhan 2019-nCoV outbreak: similarity of early epidemic and prediction of future trends. BioRxiv. 10.1101/2020.01.24.919241
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical