Thoracic ultrasound and SARS-COVID-19: a pictorial essay
- PMID: 32297175
- PMCID: PMC7159975
- DOI: 10.1007/s40477-020-00458-7
Thoracic ultrasound and SARS-COVID-19: a pictorial essay
Abstract
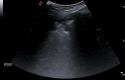
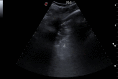
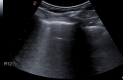
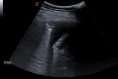
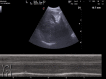
Thoracic ultrasound seems to adapt to the screening for lung involvement of patients with suspected or ascertained SARS-COVID-19 infection due to its characteristics of easy applicability. It can be also a relevant method in monitoring patients. B lines are early finding of COVID-19, even in mild-symptomatic subjects; in the most serious cases such as pre-ARDS or ARDS, the B lines end up filling the ultrasound image almost completely, until it merges, so as to create a single hyperechoic image named as "white lung", with distortion and irregularity of the pleural line. In advanced stage, lung consolidations are present, representing pulmonary pathological areas that are no longer normally ventilated.
Keywords: COVID-19; Lung; Ultrasound; Virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest and no funding sources.
Figures




References
-
- National Health Commission of People’s Republic of China (2020) Pneumonia diagnosis and treatment of 2019-nCoV infection from Chinese NHC and CDC 2020. https://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/zhengcwj/202001/4294563ed35b43209b31739bd0785.... Accessed 1 Feb 2020
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

