Non-corticosteroid immunosuppressive medications for steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome in children
- PMID: 32297308
- PMCID: PMC7160055
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002290.pub5
Non-corticosteroid immunosuppressive medications for steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome in children
Update in
-
Non-corticosteroid immunosuppressive medications for steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 8;11(11):CD002290. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002290.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39513526
Abstract
Background: About 80% of children with steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome (SSNS) have relapses. Of these children, half relapse frequently, and are at risk of adverse effects from corticosteroids. While non-corticosteroid immunosuppressive medications prolong periods of remission, they have significant potential adverse effects. Currently, there is no consensus about the most appropriate second-line agent in children who are steroid sensitive, but who continue to relapse. In addition, these medications could be used with corticosteroids in the initial episode of SSNS to prolong the period of remission. This is the fourth update of a review first published in 2001 and updated in 2005, 2008 and 2013.
Objectives: To evaluate the benefits and harms of non-corticosteroid immunosuppressive medications in SSNS in children with a relapsing course of SSNS and in children with their first episode of nephrotic syndrome.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Kidney and Transplant Register of Studies up to 10 March 2020 through contact with the Information Specialist using search terms relevant to this review. Studies in the Register are identified through searches of CENTRAL, MEDLINE, and EMBASE, conference proceedings, the International Clinical Trials Register (ICTRP) Search Portal and ClinicalTrials.gov.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) or quasi-RCTs were included if they involved children with SSNS and compared non-corticosteroid immunosuppressive medications with placebo, corticosteroids (prednisone or prednisolone) or no treatment; compared different non-corticosteroid immunosuppressive medications or different doses, durations or routes of administration of the same non-corticosteroid immunosuppressive medication.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently assessed study eligibility, risk of bias of the included studies and extracted data. Statistical analyses were performed using a random-effects model and results expressed as risk ratio (RR) for dichotomous outcomes or mean difference (MD) for continuous outcomes with 95% confidence intervals (CI). The certainty of the evidence was assessed using GRADE.
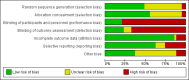
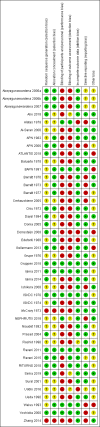
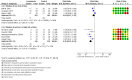
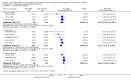
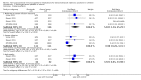
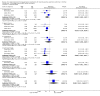
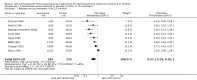
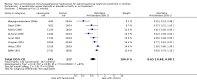
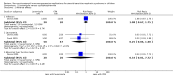
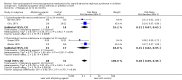
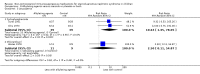
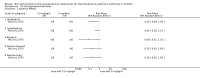
Main results: We identified 43 studies (91 reports) and included data from 2428 children. Risk of bias assessment indicated that 21 and 24 studies were at low risk of bias for sequence generation and allocation concealment respectively. Nine studies were at low risk of performance bias and 10 were at low risk of detection bias. Thirty-seven and 27 studies were at low risk of incomplete and selective reporting respectively. Rituximab (in combination with calcineurin inhibitors (CNI) and prednisolone) versus CNI and prednisolone probably reduces the number of children who relapse at six months (5 studies, 269 children: RR 0.23, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.43) and 12 months (3 studies, 198 children: RR 0.63, 95% CI 0.42 to 0.93) (moderate certainty evidence). At six months, rituximab resulted in 126 children/1000 relapsing compared with 548 children/1000 treated with conservative treatments. Rituximab may result in infusion reactions (4 studies, 252 children: RR 5.83, 95% CI 1.34 to 25.29). Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and levamisole may have similar effects on the number of children who relapse at 12 months (1 study, 149 children: RR 0.90, 95% CI 0.70 to 1.16). MMF may have a similar effect on the number of children relapsing compared to cyclosporin (2 studies, 82 children: RR 1.90, 95% CI 0.66 to 5.46) (low certainty evidence). MMF compared to cyclosporin is probably less likely to result in hypertrichosis (3 studies, 140 children: RR 0.23, 95% CI 0.10 to 0.50) and gum hypertrophy (3 studies, 144 children: RR 0.09, 95% CI 0.07 to 0.42) (low certainty evidence). Levamisole compared with steroids or placebo may reduce the number of children with relapse during treatment (8 studies, 474 children: RR 0.52, 95% CI 0.33 to 0.82) (low certainty evidence). Levamisole compared to cyclophosphamide may make little or no difference to the risk for relapse after 6 to 9 months (2 studies, 97 children: RR 1.17, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.81) (low certainty evidence). Cyclosporin compared with prednisolone may reduce the number of children who relapse (1 study, 104 children: RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.13 to 0.83) (low certainty evidence). Alkylating agents compared with cyclosporin may make little or no difference to the risk of relapse during cyclosporin treatment (2 studies, 95 children: RR 0.91, 95% CI 0.55 to 1.48) (low certainty evidence) but may reduce the risk of relapse at 12 to 24 months (2 studies, 95 children: RR 0.51, 95% CI 0.35 to 0.74), suggesting that the benefit of the alkylating agents may be sustained beyond the on-treatment period (low certainty evidence). Alkylating agents (cyclophosphamide and chlorambucil) compared with prednisone probably reduce the number of children, who experience relapse at six to 12 months (6 studies, 202 children: RR 0.44, 95% CI 0.32 to 0.60) and at 12 to 24 months (4 studies, 59 children: RR 0.20, 95% CI 0.09 to 0.46) (moderate certainty evidence). IV cyclophosphamide may reduce the number of children with relapse compared with oral cyclophosphamide at 6 months (2 studies, 83 children: RR 0.54, 95% CI 0.34 to 0.88), but not at 12 to 24 months (2 studies, 83 children: RR 0.99, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.29) and may result in fewer infections (2 studies, 83 children: RR 0.14, 95% CI 0.03 to 0.72) (low certainty evidence). Cyclophosphamide compared to chlorambucil may make little or no difference in the risk of relapse after 12 months (1 study, 50 children: RR 1.31, 95% CI 0.80 to 2.13) (low certainty evidence).
Authors' conclusions: New studies incorporated in this review indicate that rituximab is a valuable additional agent for managing children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. However, the treatment effect is temporary, and many children will require additional courses of rituximab. The long-term adverse effects of this treatment are not known. Comparative studies of CNIs, MMF, levamisole and alkylating agents have demonstrated little or no differences in efficacy but, because of insufficient power; clinically important differences in treatment effects have not been completely excluded.
Copyright © 2020 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures










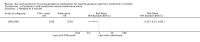
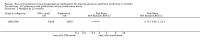







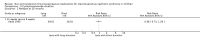
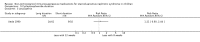



















Update of
-
Non-corticosteroid immunosuppressive medications for steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Oct 29;(10):CD002290. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002290.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Apr 16;4:CD002290. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002290.pub5. PMID: 24166716 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abeyagunawardena 2006a {published data only}
-
- Abeyagunawardena AS, Trompeter RS. Efficacy of levamisole as a single agent in maintaining remission in steroid dependant nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: COD.OC.5]. Pediatric Nephrology 2006;21(10):1503. [CENTRAL: CN‐00602129] - PubMed
Abeyagunawardena 2006b {published data only}
-
- Abeyagunawardena AS, Trompeter RS. Intravenous pulsed vs oral cyclophosphamide therapy in steroid dependant nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: COD.PP 54]. Pediatric Nephrology 2006;21(10):1535.
Abeyagunawardena 2007 {published data only}
-
- Abeyagunawardena A. Intravenous pulsed cyclophosphamide versus vincristine therapy in steroid dependant nephrotic syndrome: a randomised controlled trial [abstract no: 550P]. Pediatric Nephrology 2007;22(9):1547.
Ahn 2018 {published data only}
-
- Ahn YH, Kang HG, Kim SH. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in children with refractory nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter clinical trial [abstract]. Kidney Research & Clinical Practice 2014;33(2):A1. [CENTRAL: CN‐01657515]
-
- Anh YH, Kim SH, Han KH, Cho HY, Shin JI, Cho MH, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in children with refractory nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter clinical trial [abstract no: O39]. Pediatric Nephrology 2013;28(8):1361. [EMBASE: 71126980]
Alatas 1978 {published data only}
-
- Alatas H, Wirya IG, Tambunan T, Himawan S. Controlled trial of chlorambucil in frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome in children (a preliminary report). Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 1978;61 Suppl 1:222‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Al‐Saran 2006 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Saran K, Mirza K. Experience with levamisole in FR/SD childhood nephrotic syndrome in a large Saudi center [abstract no:PO03]. Pediatric Nephrology 2004;19(9):C93.
-
- Al‐Saran K, Mirza K, Al‐Ghanam G, Abdelkarim M. Experience with levamisole in frequently relapsing, steroid‐dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatric Nephrology 2006;21(2):201‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
APN 1982 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Arbeitsgemeinschaft fur Padiatrische Nephrologie. Effect of cytotoxic drugs in frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome with and without steroid dependence. New England Journal of Medicine 1982;306(8):451‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Brodehl J, Krohn HP, Ehrich JH. The treatment of minimal change nephrotic syndrome (lipoid nephrosis): cooperative studies of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft fur Padiatrische Nephrologie (APN). Klinische Padiatrie 1982;194(3):162‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
APN 2006 {published data only}
-
- Arbeitsgemeinschaft fur Padiatrische Nephrologie. Results of the nephrotic syndrome study VIII of the APN: new standard treatment versus new standard treatment plus 8 weeks cyclosporin A [abstract]. Pediatric Nephrology 1999;13:C26. [CENTRAL: CN‐00636143]
-
- Hoyer PF. Results of the nephrotic syndrome study VIII of the APN: new standard treatment versus new standard treatment plus 8 weeks cyclosporin A [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1999;10(Program & Abstracts):104A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00550522]
-
- Hoyer PF, Arbeitsgemeinschaft fur Padiatrische Nephrologie. The initial treatment of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome with prednisone and cyclosporin A: preliminary results of a therapeutic trial [abstract no: P147]. Pediatric Nephrology 1995;9(6):C91. [CENTRAL: CN‐00401335]
-
- Hoyer PF, Brodehl J. Initial treatment of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children: prednisone versus prednisone plus cyclosporine A: a prospective, randomized trial. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006;17(4):1151–7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ATLANTIS 2018 {published data only}
Baluarte 1978 {published data only}
-
- Baluarte HJ, Hiner L, Gruskin AB. Chlorambucil dosage in frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome: a controlled clinical trial. Journal of Pediatrics 1978;92(2):295‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
BAPN 1991 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Levamisole for corticosteroid‐dependent nephrotic syndrome in childhood. British Association for Paediatric Nephrology. Lancet 1991;337(8757):1555‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Barratt 1970 {published data only}
-
- Barratt TM, Soothill JF. A controlled trial of cyclophosphamide in steroid sensitive relapsing nephrotic syndrome of childhood [abstract]. Nephron 1971;8:95. - PubMed
-
- Barratt TM, Soothill JF. Controlled trial of cyclophosphamide in steroid‐sensitive relapsing nephrotic syndrome of childhood. Lancet 1970;296(7671):479‐2. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Barratt 1973 {published data only}
Barratt 1977 {published data only}
Cerkauskiene 2005 {published data only}
-
- Cerkauskiene R, Kaltenis P. Comparative study of prednisolone alone and prednisolone plus fusidic acid in the treatment of children with steroid‐responsive nephrotic syndrome. Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania) 2005;41 Suppl 1:26‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chiu 1973 {published data only}
-
- Chiu J, McLaine PN, Drummond KN. A controlled prospective study of cyclophosphamide in relapsing, corticosteroid‐responsive, minimal‐lesion nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Journal of Pediatrics 1973;82(4):607‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dayal 1994 {published data only}
-
- Dayal U, Dayal AK, Shastry JC, Raghupathy P. Use of levamisole in maintaining remission in steroid‐sensitive nephrotic syndrome in children.[Erratum in: Nephron 1994;67(4):507]. Nephron 1994;66(4):408‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Donia 2005 {published data only}
-
- Donia A, Ammar H, Moustafa F, Sobh M. Long‐term efficacy of two unconventional adjunctive therapies in minimal change nephrotic children [abstract no: SP062]. 41st Congress. European Renal Association. European Dialysis and Transplantation Association; 2004 May 15‐18; Lisbon, Portugal. 2004:37.
-
- Donia AF, Ammar HM, El‐Agroudy A, Moustafa F, Sobh MA. Long‐term results of two unconventional agents in steroid‐dependent nephrotic children. Pediatric Nephrology 2005;20(10):1420‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dorresteijn 2008 {published data only}
-
- Dorresteijn E, Kist‐van Holthe J, Levtchenko E, Nauta J, Hop W, Heijden B. Randomized controlled trial of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) versus cyclosporine A (CsA) in children with frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: 28FC]. Pediatric Nephrology 2007;22(9):1442. [CENTRAL: CN‐00636133]
-
- Dorresteijn E, Elburg R, Nauta J, Heijden B. Intestinal permeability in patients treated with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) for nephrotic syndrome (NS) [abstract no: 355]. Pediatric Nephrology 2010;25(9):1865‐6. [EMBASE: 70438457]
Edefonti 1988 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Edefonti A, Ghio L, Bettinelli A, Paterlini G. Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia due to cyclosporin A (CyA) administration in children with nephrotic syndrome (NS) [abstract no: F1.12]. Pediatric Nephrology 1987;1(4):C8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00465774] - PubMed
-
- Edefonti A, Ghio L, Bettinelli A, Paterlini G, Giani M, Nebbia G, et al. Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia due to ciclosporin administration in children with nephrotic syndrome. Contributions to Nephrology 1988;67:121‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Edefonti A, Ghio L, Rizzoni G, Rinaldi S, Gusmano R, Lama G, et al. Cyclosporine (CSA) vs cyclophosphamide (CYC) for children with frequently relapsing/steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome (FR/SDNS): long term study [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1992;3(3):310. [CENTRAL: CN‐00460680]
-
- Edefonti A, Ghio L, Rizzoni G, Rinaldi S, Gusmano R, Lama G, et al. Cyclosporine (CSA) vs cyclophosphamide (CYC) for children with frequently relapsing/steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome: long term study [abstract]. 9th Congress of the International Pediatric Nephrology Association; 1992 Aug 30‐Sep 4; Jerusalem, Israel. 1992:C70. [CENTRAL: CN‐00483820]
-
- Ponticelli C. A multicenter controlled prospective trial with cyclosporine vs cyclophosphamide in frequent relapsers and steroid dependent patients with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Journal of Nephrology 1989;2(2):147‐51. [EMBASE: 1991014828]
Gellermann 2013 {published data only}
-
- Gellermann J, Querfeld U. Frequently relapsing steroid‐sensitive nephrotic syndrome (SSNS) in children and adolescents: treatment with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) vs. cyclosporin A (CsA) [abstract no: OS3‐FRI‐172]. Pediatric Nephrology 2011;26(9):1579. [EMBASE: 70530472]
-
- Gellermann J, Schaefer F, Querfeld U. Serum suPAR levels are modulated by immunosuppressive therapy of minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Pediatric Nephrology 2014;29(12):2411‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Querfeld U, Gellermann J. A randomized cross‐over multicenter trial of mycophenolate mofetil versus cyslosporin A in children with frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: LB‐OR04]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2011;22(Abstracts):1‐2B. [CENTRAL: CN‐01912567] - PMC - PubMed
Grupe 1976 {published data only}
-
- Grupe WE, Makker SP, Ingelfinger JR. Chlorambucil treatment of frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 1976;295(14):746‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gruppen 2015 {published data only}
-
- Gruppen M, Bouts A, Niaudet P, Schurmans T, Knops N, Ranguelov N, et al. The levamisole study in steroid sensitive idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (SSINS): inclusion completed [abstract no: P150]. Pediatric Nephrology 2012;27(9):1712‐3. [EMBASE: 71386368]
-
- Gruppen M, Davin JC, Bouts A. Levamisole increases the time to relapse in children with steroid‐sensitive idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: Results of a multi‐center, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial [abstract no: FP‐S25‐11]. Pediatric Nephrology 2016;31(10):1753. [EMBASE: 612479674]
-
- Gruppen MP, Bouts AH, Davin JC. The levamisole study in steroid sensitive idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (SSINS): completion is approaching [abstract no: PS2‐FRI‐537]. Pediatric Nephrology 2011;26(9):1682. [EMBASE: 70530801]
-
- Gruppen MP, Bouts AH, Jansen‐van der Weide MC, Merkus MP, Zurowska A, Maternik M, et al. A randomized clinical trial indicates that levamisole increases the time to relapse in children with steroid‐sensitive idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Kidney international 2018;93(2):510‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Gruppen MP, Merkus MP, Davin JC. Levamisole in steroid‐sensitive nephrotic syndrome (SSNS): an international multicenter double‐blind randomized trial: the last news [abstract no: COD.PP40]. Pediatric Nephrology 2006;21(10):1531. [CENTRAL: CN‐01912571] - PubMed
Iijima 2011 {published data only}
-
- Iijima K. Rituximab for childhood refractory nephrotic syndrome. Pediatrics International 2011;53(5):617‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Iijima K. Rituximab for childhood‐onset, complicated, frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid‐dependent nephrotic syndrome: an investigator initiated, multicenter, double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Japanese Journal of Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2011;42(Suppl 2):S82‐4. [EMBASE: 600779881]
-
- Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K, Mori R, Tuchida M, Kamei K, et al. Rituximab for childhood‐onset, complicated, frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid‐dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentre, double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet 2014;384(9950):1273‐81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K, Tsuchida N, Tanaka R, Ishikura K, et al. Multicenter, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomized trial of rituximab for the treatment of childhood‐onset refractory nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: O‐41]. Pediatric Nephrology 2013;28(8):1362. [CENTRAL: CN‐01912565]
Iijima 2014 {published data only}
-
- Iijima K, Nakamura MS, Saito M, Ohashi Y, Yoshikawa N. Cyclosporine C2 monitoring for frequent‐relapsing nephrotic syndrome in children: a multicenter randomized controlled trial [abstract no: LB‐PO3157]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2011;22(Abstracts):6B. [CENTRAL: CN‐01912566]
-
- Iijima K, Sako M, Oba MS, Ito S, Hataya H, Tanaka R, et al. Cyclosporine C2 monitoring for the treatment of frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome in children: a multicenter randomized phase II trial. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN 2014;9(2):271‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nakamura MS, Iijima K, Oba MS, Honda M, Nakamura H, Nagata M, et al. Cyclosporine C2 monitoring for the treatment of frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome in children: a multicenter randomized trial [abstract no: P‐SUN191]. Pediatric Nephrology 2013;28(8):1596.
Ishikura 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ishikura K, Ikeda M, Hattori S, Yoshikawa N, Sasaki S, Iijima K, et al. Effective and safe treatment with cyclosporine in nephrotic children: a prospective, randomized multicenter trial. Kidney International 2008;73(10):1167‐73. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Ishikura K, Ikeda M, Hattori S, Yoshikawa N, Sasaki S, Ijima K, et al. A 2‐year, prospective, randomized, multicenter trial of cyclosporine in children with frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: 497P]. Pediatric Nephrology 2007;22(9):1531. [CENTRAL: CN‐00653771]
-
- Ishikura K, Yoshikawa N, Nakazato H, Sasaki S, Nakanishi K, Matsuyama T, et al. Morbidity in children with frequently relapsing nephrosis: 10‐year follow‐up of a randomized controlled trial. Pediatric Nephrology 2015;30(3):459‐68. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ISKDC 1970 {published data only}
-
- Abramowicz M, Barnett HL, Edelmann CM Jr, Greifer I, Kobayashi O, Arneil GC, et al. Controlled trial of azathioprine in children with nephrotic syndrome. A report for the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Lancet 1970;1(7654):959‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Arneil GC. International trial of azathioprine in nephrotic syndrome in childhood [abstract]. Nephron 1971;8:95. [CENTRAL: CN‐00602053]
ISKDC 1974 {published data only}
-
- Prospective, controlled trial of cyclophosphamide therapy in children with nephrotic syndrome. Report of the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Lancet 1974;304(7878):423‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
McCrory 1973 {published data only}
-
- McCrory WW, Shibuya M, Lu WH, Lewy JE. Therapeutic and toxic effects observed with different dosage programs of cyclophosphamide in treatment of steroid‐responsive but frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome. Journal of Pediatrics 1973;82(4):614‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
NEPHRUTIX 2018 {published data only}
-
- Boumediene A, Vachin P, Sendeyo K, Oniszczuk J, Zhang SY, Henique C, et al. NEPHRUTIX: A randomized, double‐blind, placebo vs rituximab‐controlled trial assessing T‐cell subset changes in minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Journal of Autoimmunity 2018;88:91‐102. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Niaudet 1992 {published data only}
-
- Niaudet P. Comparison of cyclosporin and chlorambucil in the treatment of steroid‐dependent idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: a multicentre randomized controlled trial. The French Society of Paediatric Nephrology. Pediatric Nephrology 1992;6(1):1‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Prasad 2004 {published data only}
-
- Prasad N, Gulati S, Sharma RK, Singh U, Ahmed M. Pulse cyclophosphamide therapy in steroid‐dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatric Nephrology 2004;19(5):494‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rashid 1996 {published data only}
-
- Rashid HU, Ahmed S, Fatima N, Khanam A. Levamisole in the treatment of steroid dependent or frequent relapsing nephrotic syndrome in children. Bangladesh Renal Journal 1996;15(1):6‐8. [EMBASE: 1996266847]
Ravani 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ravani P, Magnasco A, Edefonti A, Murer L, Rossi R, Ghio L, et al. Short‐term effects of rituximab in children with steroid‐ and calcineurin‐dependent nephrotic syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN 2011;6(6):1308‐15. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Ravani 2015 {published data only}
RITURNS 2018 {published data only}
-
- Basu A, Sander A, Preussler S, Sinha Mahapatra T, Schaefer F. Long‐term efficacy of rituximab & MMF maintenance ‐ therapy in childhood SDNS [abstract no: IPN11036‐82]. Pediatric Nephrology 2019;34(10):2003.
-
- Basu B. Randomized clinical trial to compare efficacy and safety of rituximab to that of calcineurin inhibitor in children with steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome. Protocol version 1.2 (final version). www.jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/2685284?resultCl... (accessed 4 March 2020).
-
- Schaefer F. Superior efficacy of rituximab vs tacrolimus in pediatric steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome [abstract]. 54th ERA‐EDTA Congress; 2017 June 3‐6; Madrid, Spain. 2017.
Sinha 2019 {published data only}
-
- Bagga A, Bhatia D, Puraswani M, Hari P, Sinha A. Randomized trial comparing efficacy & safety of mycophenolate mofetil and levamisole in frequently relapsing & steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: P‐SUN199]. Pediatric Nephrology 2013;28(8):1599‐600. [EMBASE: 71127678]
-
- Sinha A, Peruswami M, Rawat M, Hari P, Bagga A. Randomized controlled trial to compare the efficacy and safety of mycophenolate mofetil versus levamisole in children with frequently relapsing and steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome [abstract]. Pediatric Nephrology 2015;29(12):2434. [CENTRAL: CN‐01912558]
-
- Sinha A, Puraswani M, Kalaivani M, Goyal P, Hari P, Bagga A. Efficacy and safety of mycophenolate mofetil versus levamisole in frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome: an open‐label randomized controlled trial. Kidney International 2019;95(1):2010‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sural 2001 {published data only}
-
- Sural S, Pahari DK, Mitra K, Bhattacharya S, Mondal S, Taraphder A. Efficacy of levamisole compared to cyclophosphamide and steroid in frequently relapsing (FR) minimal change nephrotic syndrome (MCNS) [abstract no: A0660]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(Program & Abstracts):126A.
Uddin 2016 {published data only}
-
- Uddin GM, Rahman MA, Rahman MH, Roy RR, Begum A, Huque SS. Comparative efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil and cyclosporine in children with frequent relapse nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: PO‐276]. Pediatric Nephrology 2016;31(10):1852‐3. [EMBASE: 612479647]
Ueda 1990 {published data only}
Weiss 1993 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Weiss R. Results of a randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled, multi‐center clinical trial of levamisole for the treatment of children with frequently relapsing or steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome. Personal communication 2005.
-
- Weiss R, NY, NJ, Phila. Pediatric Nephrology Study Group. Randomized, double‐blind, placebo (P) controlled trial of levamisole (L) for children (CH) with frequently relapsing/steroid dependant (FR/SD) nephrotic syndrome (NS) [abstract no: 98P]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1993;4(Program & Abstracts):289. [CENTRAL: CN‐00520404]
Yoshioka 2000 {published data only}
-
- Yoshioka K, Ohashi Y, Sakai T, Ito H, Yoshikawa N, Nakamura H, et al. A multicenter trial of mizoribine compared with placebo in children with frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome. Kidney International 2000;58(1):317‐24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Yoshioka K, Ohashi Y, Sakai T, Ito H, Yoshikawa N, Nakamura H, et al. Placebo‐controlled trial of mizoribine (MZR) in children with frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome (FRNS). The Pediatric Mizoribine Study Group [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1998;9(Program & Abstracts):163A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00448484]
Zhang 2014 {published data only}
-
- Zhang B, Liu T, Wang W, Zhang X, Fan S, Liu Z, et al. A prospective randomly controlled clinical trial on azithromycin therapy for induction treatment of children with nephrotic syndrome. European Journal of Pediatrics 2014;173(4):509‐15. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Zhang BL, Liu T. A prospective clinical randomized controlled trial on azithromycin therapy in induction treatment in children with nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: O‐44]. Pediatric Nephrology 2013;28(8):1364. [EMBASE: 71126985]
References to studies excluded from this review
Arun 2009 {published data only}
-
- Arun S, Bagga A, Bhatnagar S, Hari P, Menon S, Saini S. Efficacy of zinc (Zn) in reducing relapses in steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome (SSNS): double blind, randomized controlled trial (RCT) (CRG030600044) [abstract no: 184]. Pediatric Nephrology 2007;22(9):1481. [CENTRAL: CN‐00724915] - PubMed
-
- Arun S, Bhatnagar S, Menon S, Saini S, Hari P, Bagga A. Efficacy of zinc supplements in reducing relapses in steroid‐sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Pediatric Nephrology 2009;24(8):1583‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Basu 2015 {published data only}
-
- Basu B, Pandey R, Mahapatra TK, Mondal N, Schaefer F. WITHDRAWN: Efficacy and safety of mycophenolate mofetil versus levamisole in children and adolescents with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: results of a randomized clinical trial. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2015 Jun 09. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Basu B, Pandey R, Mishra OP. WITHDRAWN: Randomized controlled trial to compare the efficacy & safety of mycophenolate mofetil vs levamisole in children with frequent relapsing & steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: O‐18]. Pediatric Nephrology 2013;28(8):1353. [CENTRAL: CN‐01658385]
-
- Basu B, Pandey R, Mondal N, Schaefer F. WITHDRAWN: Efficacy and safety of mycophenolate‐mofetil vs levamisole in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: results of a randomized clinical trial [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2014;29(Suppl 3):iii7. [EMBASE: 71491485]
Beige 2003 {published data only}
-
- Beige J, Moosmayer I, Liefeldt L, Neumayer HH, Zidek W, Peters H. Effective and safe treatment of primary nephrotic syndrome with tacrolimus (FK 506) [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2003;18(Suppl 4):65. [CENTRAL: CN‐00444378]
Cerkauskiene 2004 {published data only}
-
- Cerkauskiene R, Jankauskiene A, Kaltenis P. Effect of omega‐3 fatty acids on serum homocysteine in childhood steroid‐sensitive nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: P011]. Pediatric Nephrology 2004;19(9):C95.
Dharmaraj 2009 {published data only}
-
- Dharmaraj R, Hari P, Bagga A. Randomized cross‐over trial comparing albumin and frusemide infusions in nephrotic syndrome. Pediatric Nephrology 2009;24(4):775‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hari P, Bagga A. Does albumin infusion augment frusemide induced diuresis in edematous children with nephrotic syndrome? [abstract no: M‐PO‐0834]. 4th World Congress of Nephrology.19th International Congress of the International Society of Nephrology (ISN); 2007 Apr 21‐25; Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. 2007:285.
Fong 1997 {published data only}
-
- Fong GZ. Observation on refractory nephrotic syndrome with integrated traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) ‐ Western medicine (WM) [abstract]. Nephrology 1997;3(Suppl 1):S125. [CENTRAL: CN‐01912560]
Hu 2008a {published data only}
-
- Hu GH, Yi ZW, Wang JH, Yao JC. Effect of Triptergium wilfordii polyglycosidium on content of Th1 and Th2 in child recurrent nephrotic syndrome. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi [China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica] 2008;33(4):441‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Khemani 2016 {published data only}
-
- Khemani S, Moorani KN. Cyclosporine versus cyclophosphamide in childhood nephrotic syndrome. Journal of the Liaquat University of Medical & Health Sciences 2016;15(2):57‐62. [EMBASE: 611436094]
Kirubakaran 1984 {published data only}
-
- Kirubakaran MG, Jacob GK, Date A, Shastry JC. A controlled trial of levamisole in frequently relapsing minimal change disease [abstract]. Kidney International 1984;26(2):240. [CENTRAL: CN‐01912563]
Li 1994 {published data only}
-
- Li X, Li Z, Cheng Z. Treatment of children with simple nephrotic syndrom using prednison once per day. Acta Academiae Medicinae Hubei 1994;15(4):386‐8. [EMBASE: 1995005617]
Li 2005a {published data only}
-
- Li X, Tian J, Lin W, He X, Jiang H, Chen J. Mycophenolate mofetil therapy in primary nephrotic syndrome with hepatitis B virus infection [abstract no: F‐PO1010]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2005;16:557A. [CENTRAL: CN‐01912562]
Liu 2016c {published data only}
-
- Liu Y, Qu X, Chen W, Zhang Y, Liu L. Efficacy of leflunomide combined with prednisone in the treatment of refractory nephrotic syndrome. Renal Failure 2016;38(10):1616‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lou 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lou T, Wang C, Chen Z, Tang H, Liu X, Yu X. Randomized controlled trial of leflunomide in the treatment of refractory nephrotic syndrome [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2004;15:353A. [CENTRAL: CN‐01912561]
Naigui 1997 {published data only}
-
- Naigui X, Jian X, Jing H. A clinical study on low dose cyclosporin A with diltiazem in the treatment of primary nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: P203]. Nephrology 1997;3 Suppl(1):S125. [CENTRAL: CN‐00461383]
NCT02390362 {published data only}
-
- Greenbaum L, Smoyer W. Randomized trial comparing rituximab against mycophenolate mofetil in children wtih refractory nephrotic syndrome (RAMP). www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02390362 (first received 17 March 2015).
Ni 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ni ZH, Qian JQ, Lin AW, Mu S, Zhu ML, Fang W. A controlled, prospective study of efficacy of leflunomide in patients with nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: SA‐PO1025]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2003;14(Nov):524A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00520368]
Nishiyama 1997 {published data only}
-
- Nishiyama J, Nakabayashi I, Moriya H, Kikuchi Y, Yoshizawa N. Effect of combined treatment with methylprednisolone pulse and nafamostat mesilate for nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: P221]. Nephrology 1997;3(Suppl 1):S130. [CENTRAL: CN‐01912557]
Pecoraro 2003 {published data only}
-
- Pecoraro C, Caropreso MR, Malgieri G, Ferretti A, Nuzzi F. Therapy of first episode steroid responsive nephrotic syndrome (FESRNS): a randomised controlled trial [abstract no: MP087]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2005;20(Suppl 5):v230.
-
- Pecoraro C, Caropreso MR, Malgieri G, Ferretti AV, Raddi G, Piscitelli A, et al. Therapy of first episode of steroid responsive nephrotic syndrome: a randomised controlled trial [abstract no: OFC41]. Pediatric Nephrology 2004;19(9):C72. [CENTRAL: CN‐00644160]
-
- Pecoraro C, Caropreso MR, Passaro G, Ferretti AV, Malgieri G. Therapy of first episode of steroid responsive nephrotic syndrome: a randomised controlled trial [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2003;18(Suppl 4):63. [CENTRAL: CN‐00447140]
Rowe 1990 {published data only}
-
- Rowe PC, McLean RH, Ruley EJ, Salcedo JR, Baumgardner RA, Zaugg B, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin in minimal change nephrotic syndrome: a crossover trial. Pediatric Nephrology 1990;4(1):32‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Samuels 2002 {published data only}
-
- Samuels R, Mani UV, Iyer UM, Nayak US. Hypocholesterolemic effect of spirulina in patients with hyperlipidemic nephrotic syndrome. Journal of Medicinal Food 2002;5(2):91‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sancewicz‐Pach 1995 {published data only}
-
- Sancewicz‐Pach K, Slowiaczek E, Kwinta‐Rybicka J, Wilkosz K, Nowak J. Results for 8‐week and 12‐month cyclosporin A treatment in children with primary nephrotic syndrome [abstract]. XIIIth International Congress of Nephrology; 1995 Jul 2‐6; Madrid, Spain. 1995:270.
Sasinka 1976 {published data only}
-
- Sasinka M, Plenta I, Kaiserova E, Izakovic V, Pavlovic M, CYTEMBENA/*THER USE, et al. Comparison of the effectiveness of cyclophosphamide and cytembena in controlled clinical trial in nephrotic syndrome and chronic glomerulonephritis [Porovnanie ucinnosti Cyclophosphamidu a Cytembeny v kontrolovanom klinickom pokuse pri nefrotickom syndrome a chronickej glomerulonefritide]. Ceskoslovenska Pediatrie 1976;31(3):127‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shendurnikar 2004 {published data only}
-
- Shendurnikar N, Agrawal N, Nayak US, Samuels R, Mani UV. Spirulina supplementation in pediatric nephrotic syndrome [abstract]. Pediatric Nephrology 2004;19(9):C105. [CENTRAL: CN‐01912556]
Stavrovskaya 2001 {published data only}
-
- Stavrovskaya E, Neverov N, Shvetsov M, Tareeva I. Angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) and angiotensin 2 receptor blockers (ARB) attenuate hypercholesterolemia in patients with chronic nephrotic glomerulonephritis [abstract]. 38th Congress of the European Renal Association European Dialysis & Transplant Association; 2001 Jun 24‐27; Vienna, Austria. 2001:96. [CENTRAL: CN‐00461795]
Tejani 1988 {published data only}
-
- Tejani A, Gonzalez R, Rajpoot D, Sharma R, Pomrantz A. A randomized trial of cyclosporine with low‐dose prednisone compared with high‐dose prednisone in nephrotic syndrome. Transplantation Proceedings 1988;20(3 Suppl 4):262‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Tejani A, Suthanthiran M, Pomrantz A. A randomized controlled trial of low‐dose prednisone and ciclosporin versus high‐dose prednisone in nephrotic syndrome of children. Nephron 1991;59(1):96‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Tejani A, Suthanthiran M, Rajpoot D, Gonzalez R, Pomrantz A. Randomized trial of cylosporine and low dose prednisone (P&CS) vs conventional prednisone (P) therapy in recent onset (< 1 yr) nephrotic syndrome (NS) [abstract]. Kidney International 1989;35(1):213. [CENTRAL: CN‐01912553]
Trompeter 1978 {published data only}
Urdaneta 1983 {published data only}
-
- Urdaneta Carruyo E, Zuniga Armendariz V, Gordillo Paniagua G. Therapeutic trial with levamisole in children with idiopathic minimal change nephrotic syndrome [Ensayo terapeutico con levamisol en ninos con sindrome nefrotico idiopatico de lesiones glomerulares minimas]. Boletin Medico del Hospital Infantil de Mexico 1983;40(2):82‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wang 2005 {published data only}
Wu 2015 {published data only}
-
- Wu B, Mao J, Shen H, Fu H, Wang J, Liu A, et al. Triple immunosuppressive therapy in steroid‐resistant nephrotic syndrome children with tacrolimus resistance or tacrolimus sensitivity but frequently relapsing. Nephrology 2015;20(1):18‐24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yamashita 1971 {published data only}
-
- Yamashita F, Funatsu T, Nagayama K, Arihiro H, Anan S. Evaluation of alternate‐day steroid therapy for nephrotic syndrome in childhood by cross‐over study. Kurume Medical Journal 1971;18(3):153‐60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yi 2008 {published data only}
-
- Yi ZW, Wu XC, Xu H, Zhou LJ, Wu YB, Feng SP, et al. A prospective multicenter clinical control trial on treatment of refractory nephrotic syndrome with mycophenolate mofetil in children. Zhongguo Dangdai Erke Zazhi 2008;10(5):575‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zedan 2016 {published data only}
-
- Zedan MM, El‐Refaey A, Zaghloul H, Abdelrahim ME, Osman A, Zedan MM, et al. Montelukast as an add‐on treatment in steroid dependant nephrotic syndrome, randomised‐controlled trial. Journal of Nephrology 2016;29(4):585‐92. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zhang 2007d {published data only}
-
- Zhang Y, Huang JP, Xiao HJ, Ding J, Yao Y, Yang JY. Prospective clinical randomized controlled trial of pulse methylprednisolone therapy in children with steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: 797]. Pediatric Nephrology 2007;22(9):1609. [CENTRAL: CN‐01912552]
Zhi‐Hong 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zhi‐Hong H, Ying D, Li Y. Effect of the astragalus injection on urine protein in children nephrotic syndrome [abstract]. Pediatric Nephrology 2004;19(9):C97.
Zhong 2007 {published data only}
-
- Zhong ZM, Yu L, Weng ZY, Hao ZH, Zhang L, Zhang YX, et al. Therapeutic effect of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract on hypercholestrolemia in children with nephrotic syndrome. Nanfang Yeie Daxue Xuebao [Journal of Southern Medical University] 2007;27(5):682‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zhu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Zhu S, Wu X. A study of leflunomide in treatment of juvenile refractory nephropathy syndrome [abstract]. Pediatric Nephrology 2013;28(8):1419. [EMBASE: 71127146]
Zou 1997 {published data only}
-
- Zou HQ, Wang YQ. Mechanism that Chinese traditional medicine reduces relapses of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS) in children [abstract]. Nephrology 1997;3(Suppl 1):S124. [CENTRAL: CN‐01912341]
References to studies awaiting assessment
NCT01092962 {published data only}
-
- Baudouin V. Cyclophosphamide versus mycophenolate mofetil for children with steroid‐dependent idiopathic nephrotic syndrome : a multicenter randomized controlled trial. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01092962 (first received 25 March 2010).
NCT01895894 {published data only}
-
- Kang HG. A prospective, randomized, open‐label study evaluating the efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil in the prevention of relapse of steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome in children. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01895894 (first received 11 July 2013).
Sawires 2019 {published data only}
-
- Sawires H, Abdelaziz H, Ahmed HM, Botrous O, Agban M. Randomized controlled trial on immunomodulatory effects of azithromycin in children with steroid‐dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatric Nephrology 2019;34(9):1591‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Sawires H, Abdelaziz H, Mostafa O, Botrous O, Agban M. Randomized controlled trial on immunomodulatory effects of azithromycin in children with steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: IPN10189‐90]. Pediatric Nephrology 2019;34(10):1933. - PubMed
Tohjoh 1994 {published data only}
-
- Tohjoh S, Narita M, Koyama T, Miyahara M, Nagasawa T, Kitagawa T, et al. Clinical evaluation of cyclosporin in the treatment of nephrotic syndrome: multicentre double‐blind study. Jin Tohseki 1994;37:565‐608.
References to ongoing studies
Hama 2018 {published data only}
Horinouchi 2018 {published data only}
-
- Horinouchi T, Sako M, Nakanishi K, Ishikura K, Ito S, Nakamura H, et al. Study protocol: mycophenolate mofetil as maintenance therapy after rituximab treatment for childhood‐onset, complicated, frequently‐relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid‐dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial (JSKDC07). BMC Nephrology 2018;19(1):302. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
INTENT 2018 {published data only}
-
- Benz MR, Doetsch J, Ehren R, Gellermann J, Haffner D, Hoyer PF, et al. Protocol of an open, randomized, controlled, multicenter trial on the initial treatment of idiopathic steroid‐sensitive nephrotic syndrome in children with mycophenolate mofetil vs. prednisone: the Intent Study [abstract no: P176]. Pediatric Nephrology 2014;29(9):1740. [EMBASE: 71662573]
-
- Ehren R, Benz MR, Doetsch J, Fichtner A, Gellermann J, Haffner D, et al. Initial treatment of steroid‐sensitive idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children with mycophenolate mofetil versus prednisone: protocol for a randomised, controlled, multicentre trial (INTENT study). BMJ Open 2018;8(10):e024882. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tonshoff B. Initial treatment of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children with mycophenolate mofetil vs. prednisone: a randomized, controlled, multicenter study (INTENT Study): Clinical study protocol: Version 4.0/20150325. www.intent‐study.de/.cm4all/iproc.php/Studienprotokoll_INTENT_V4_2015_03_25_signier... (accessed 4 March 2020).
JSKDC 10 2019 {published data only}
-
- Nagano C, Sako M, Kamei K, Ishikura K, Nakamura H, Nakanishi K, et al. Study protocol: multicenter double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial of rituximab for the treatment of childhood‐onset early‐stage uncomplicated frequently relapsing or steroid‐dependent nephrotic syndrome (JSKDC10 trial). BMC Nephrology 2019;20(1):293. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
LEARNS 2019 {published data only}
-
- Veltkamp F, Khan DH, Reefman C, Veissi S, Oers HA, Levtchenko E, et al. Prevention of relapses with levamisole as adjuvant therapy in children with a first episode of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: study protocol for a double blind, randomised placebo‐controlled trial (the LEARNS study). BMJ Open 2019;9(8):e027011. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Veltkamp F, Reefman C, Khan DH, Veissi S, Haverman L, Mathot RA, et al. Prevention of relapses with levamisole as adjuvant therapy to corticosteroids in children with a first episode of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome – an international, double blind, placebo‐controlled randomized trial [abstract no: O‐327]. Pediatric Nephrology 2018;33(10):1938.
NCT02818738 {published data only}
-
- Dossier C. Efficiency of levamisole for maintaining remission after the first flare of steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome in children (NEPHROVIR3). www.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02818738 (first received 30 June 2016).
NCT02972346 {published data only}
-
- Li Y. Availability study of ACTH to treat children SRNS/SDNS. www.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02972346 (first received 23 November 2016).
Ravani 2017 {published data only}
RITURNS II 2019 {published data only}
-
- Basu B. Compare efficacy and safety of repeated courses of rituximab to that of maintenance mycophenolate mofetil following single course of rituximab among children with steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome (RITURNS II). www.clinicaltrials gov/ct2/show/NCT03899103 (first received 2 April 2019).
RITUXIVIG 2018 {published data only}
-
- Hogan J, Deschenes G. Efficacy and safety of immunoglobulin associated with rituximab versus rituximab alone in childhood‐onset steroid‐dependent nephrotic syndrome (RITUXIVIG). www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03560011 (first received 18 June 2018).
Sinha 2019b {published data only}
-
- Sinha A, Raut S, Ghanapriya K, Bhardwaj M, Kalra S, Hari P, et al. Alternate‐day prednisolone made daily during infections versus levamisole for frequently‐relapsing nephrotic syndrome [abstract no: IPN12086‐88]. Pediatric Nephrology 2019;34(10):2171‐2.
Additional references
Arneil 1961
-
- Arneil GC. 164 children with nephrosis. Lancet 1961;2(7212):1103‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Choudhry 2009
-
- Choudhry S, Bagga A, Panka H, Sharma S Kalaivani M, Dinda A. Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus versus cyclosporine in children with steroid‐resistant nephrotic syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2009;53(5):760‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Coutinho 2001
Crowther 2010
El Bakkali 2011
Fairley 1972
-
- Fairley KF, Barrie JU, Johnson W. Sterility and testicular atrophy related to cyclophosphamide therapy. Lancet 1972;1(7750):568‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
French NS Guideline 2008
-
- Haute Autorité de Santé. Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children. National protocol for diagnosis and treatment for a rare disease [Syndrome néphrotique idiopathique de l’enfant. Protocole national de diagnostic et de soins pour une maladie rare]. http://www.has‐sante.fr/portail/upload/docs/application/pdf/2008‐06/pnds_sni_enfant.pdf (accessed prior to 4 March 2020).
Gipson 2009
-
- Gipson DS, Massengill SF, Yao L, Nagaraj S, Smoyer WE, Mahan JD, et al. Management of childhood onset nephrotic syndrome. Pediatrics 2009;124(2):747‐57. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Glenton 2010
-
- Glenton C, Santesso N, Rosenbaum S, Nilsen E, Rader T, Ciapponi A, et al. Presenting the results of Cochrane Systematic Reviews to a consumer audience: a qualitative study. Medical Decision Making 2010;30(5):566‐77. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
GRADE 2008
GRADE 2011
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction‐GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):383‐94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hahn 2015
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hogg 2003
-
- Hogg R, Fitzgibbons L, Bruick J, Bunke M, Ault B, Baqi N, et al. Multicenter trial of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) in children with steroid dependent (SD) or frequent relapsing (FR) nephrotic syndrome (NS). Report of the Southwest Pediatric Nephrology Study Group [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2003;18(Suppl 4):261.
IPNS‐IAP 2008
-
- Indian Pediatric Nephrology Group‐Indian Academy of Pediatrics, Bagga A, Ali U, Banerjee S, Kanitkar M, Phadke KD, et al. Management of steroid‐sensitive nephrotic syndrome: revised guidelines. Indian Pediatrics 2008;45(3):203‐14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ISKDC 1978
-
- Nephrotic syndrome in children: prediction of histopathology from clinical and laboratory characteristics at time of diagnosis. A report of the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Kidney International 1978;13(2):159‐65. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ISKDC 1982
-
- Nephrotic syndrome in children: a randomized trial comparing two prednisone regimens in steroid‐responsive patients who relapse early. Report of the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Journal of Pediatrics 1982;95(2):239‐43. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Japanese Guideline 2014
KDIGO 2012
-
- KDIGO Glomerulonephritis Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for glomerulonephritis. Kidney International Supplements 2012;2(2):139‐274. [www.kdigo.org/wp‐content/uploads/2017/02/KDIGO‐2012‐GN‐Guideline‐English...
Kemper 2001
-
- Kemper M, Wolf G, Müller‐Wiefel D. Transmission of glomerular permeability factor from a mother to her child. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;344(5):386‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Koskimies 1982
McKinney 2001
-
- McKinney PA, Feltbower RG, Brocklebank JT, Fitzpatrick MM. Time trends and ethnic patterns of childhood nephrotic syndrome in Yorkshire, UK. Pediatric Nephrology 2001;16(12):1040‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Moher 1998
-
- Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Moher M, et al. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta‐analyses?. Lancet 1998;352(9128):609‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Noone 2018
-
- Noone DG, Iijima K, Parekh R. Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children. Lancet 2018;392(10143):61‐74. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Querfeld 2018
-
- Querfeld U, Weber LT. Mycophenolate mofetil for sustained remission in nephrotic syndrome. Pediatric Nephrology 2018;33(12):2253‐65. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Queshi 1972
-
- Queshi MS, Pennington JH, Goldsmith HJ, Cox PE. Cyclophosphamide therapy and sterility. Lancet 972;2(7790):1290‐1. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rapola 1973
-
- Rapola J, Koskimies O, Huttunen NP, Floman P, Vilska J, Hallman N. Cyclophosphamide and the pubertal testis. Lancet 1973;1(7794):98‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Savin 1996
-
- Savin VJ, Sharma J, Sharma M, McCarthy ET, Swan SK, Ellis E, et al. Circulating factor associated with increased glomerular permeability to albumin in recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. New England Journal of Medicine 1996;354(14):878‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schlesinger 1968
-
- Schlesinger ER, Sultz HA, Mosher WE, Feldman JG. The nephrotic syndrome: its incidence and implications for the community. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1968;116(6):623‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273(5):408‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schunemann 2011a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and 'Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Schunemann 2011b
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
SINePe Consensus 2017
-
- Pasini A, Benetti E, Conti G, Ghio L, Lepore M, Massella L, et al. The Italian Society for Pediatric Nephrology (SINePe) consensus document on the management of nephrotic syndrome in children: Part I ‐ Diagnosis and treatment of the first episode and the first relapse. Italian Journal of Pediatrics 2017;43(1):41. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Sinha 2006
-
- Sinha MD, MacLeod R, Rigby E, Clark AG. Treatment of severe steroid‐dependent nephrotic syndrome (SDNS) in children with tacrolimus. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2006;21(7):1848‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sureshkumar 2014
-
- Sureshkumar P, Hodson EM, Willis NS, Barzi F, Craig JC. Predictors of remission and relapse in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: a prospective cohort study. Pediatric Nephrology 2014;29(6):1039‐46. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tarshish 1997
-
- Tarshish P, Tobin JN, Bernstein J, Edelmann CM Jr. Prognostic significance of the early course of minimal change nephrotic syndrome: report of the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1997;8(5):769‐76. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wang 2012
-
- Wang W, Xia Y, Mao J, Chen Y, Wang D, Shen H, et al. Treatment of tacrolimus or cyclosporine A in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatric Nephrology 2012;27(11):2073‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wong 2007
-
- Wong W. Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in New Zealand children, demographic, clinical features, initial management and outcome after twelve‐month follow‐up: results of a three‐year national surveillance study. Journal of Paediatrics & Child Health 2007;43(5):337‐41. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Durkan 2000
Durkan 2001a
Durkan 2001b
-
- Durkan AM, Hodson EM, Willis NS, Craig JC. Immunosuppressive agents in childhood nephrotic syndrome: a meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Kidney International 2001;59(5):1919‐27. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Durkan 2005
Hodson 2008
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

