Regenerative Metaplastic Clones in COPD Lung Drive Inflammation and Fibrosis
- PMID: 32298651
- PMCID: PMC7294989
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.047
Regenerative Metaplastic Clones in COPD Lung Drive Inflammation and Fibrosis
Abstract
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive condition of chronic bronchitis, small airway obstruction, and emphysema that represents a leading cause of death worldwide. While inflammation, fibrosis, mucus hypersecretion, and metaplastic epithelial lesions are hallmarks of this disease, their origins and dependent relationships remain unclear. Here we apply single-cell cloning technologies to lung tissue of patients with and without COPD. Unlike control lungs, which were dominated by normal distal airway progenitor cells, COPD lungs were inundated by three variant progenitors epigenetically committed to distinct metaplastic lesions. When transplanted to immunodeficient mice, these variant clones induced pathology akin to the mucous and squamous metaplasia, neutrophilic inflammation, and fibrosis seen in COPD. Remarkably, similar variants pre-exist as minor constituents of control and fetal lung and conceivably act in normal processes of immune surveillance. However, these same variants likely catalyze the pathologic and progressive features of COPD when expanded to high numbers.
Keywords: COPD; chronic lung disease; fibrosis; inflammation; lung; metaplasia; myofibroblasts; neutrophils; p63; single cell cloning; stem cells.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests W.X., F.D.M., W.R., S.W., J.X., M.D., and M.V. have filed patents related to technologies used in the present work. M.V., F.D.M., and W.X. have financial interests in Nüwa Medical Systems, Houston, TX, USA and Tract pharmaceuticals, Houston, TX, USA. Nuwa Medical Systems is a trade name of Tract Pharmaceuticals.
Figures
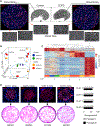

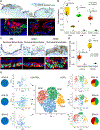

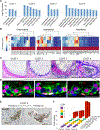
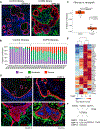

References
-
- Araya J, and Nishimura SL (2010). Fibrogenic reactions in lung disease. Annu Rev Pathol 5, 77–98. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ (2016). Inflammatory mechanisms in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 138, 16–27. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ, Burney PG, Silverman EK, Celli BR, Vestbo J, Wedzicha JA, and Wouters EF (2015). Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1, 15076. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL149678/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA228550/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL157100/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK054759/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK047967/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL129795/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL108808/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA241600/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL136961/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK115445/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES005605/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL136370/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138510/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

