Epidemiology of COVID-19
- PMID: 32299206
- PMCID: PMC7195982
- DOI: 10.3906/sag-2004-172
Epidemiology of COVID-19
Abstract
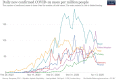
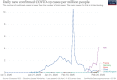
It seems that coronaviruses take an important place in the 21th century history. Five of seven human coronavirus was isolated in this century. Unfortunately, last three of them entered our life with a fear of outbreak, pandemic or death. Last human coronavirus which emerged world from Wuhan China, SARS CoV-2 and its clinical expression, Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) recently taken a significant place in our daily practice. Initial reports showed that, its origin was bats. It transmitted human to human by droplet and contact routes, but some doubt about airborne, fecal or intrauterine transmission also should be removed. Its R0 value is 2.3 but it could be as high as 5.7. Its case fatality rate was 6.3, but it was different in different ages and counties, and it could be over 15%. According to early models total 10–12 weeks is required to control an outbreak in the community. While different countries show different daily case numbers, total number of case, case mortality rates or R0, it seems they show a similar epidemic curve. Every day we learn new data about the current outbreak. Since the outbreak is not over yet, every detail should be evaluated carefully and the updates should be followed closely to monitor the epidemiological properties of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS CoV-2.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Conflict of interest statement
none declared
Figures
References
-
- Fung TS Liu DX Human coronavirus: host-pathogen interaction. Annual Review of Microbiology. 2019;73:529–557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous