Risk of falls in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 32300681
- PMCID: PMC7155375
Risk of falls in chronic kidney disease
Abstract
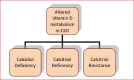
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is known to be an important risk factor for accidental, low-energy falls especially among elder individuals. The high incidence of falls is a major cause of morbidity and mortality with a substantial annual cost. Patients suffering from CKD are more prone to fall and develop fractures than the general population. Multiple risk factors have been identified and analyzed in order to explain this fact, such as drug combination, diabetes mellitus, orthostatic hypotension, vitamin D deficiency, sarcopenia and anemia, all very common in CKD. In this mini review of published evidence, we tried to search and present a complete aspect of the problem called 'Falls in Chronic Kidney Disease', focusing especially on the risk factors, discussing each one separately and its association with low- energy falls. Concluding, we discuss potential therapies and treatment goals based on the pathophysiology of CKD and accidental falls and propose new fields of investigation.
Keywords: Accidental falls; Chronic kidney disease; End stage renal disease; Hemodialysis.
Copyright: © 2017 Hylonome Publications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tinetti ME, Speechley M, Ginter SF. Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in the community. N Engl J Med. 1988;319(26):1701–7. - PubMed
-
- Cook WL, Tomlinson G, Donaldson M, Markowitz SN, Naglie G, Sobolev B, Jassal SV. Falls and Fall-Related Injuries in Older Dialysis Patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;1(6):1197–204. - PubMed
-
- Cook WL, Jassal SV. Prevalence of falls among seniors maintained on hemodialysis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2005;37(3):649–52. - PubMed
-
- Tinetti ME, Speechley M. Prevention of falls among the elderly. N Engl J Med. 1989;320(16):1055–9. - PubMed
-
- Woolcott JC, Richardson KJ, Wiens MO, Patel B, Marin J, Khan KM, et al. Meta-analysis of the Impact of 9 Medication Classes on Falls in Elderly Persons. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169(21):1952–1960. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources