Highly sensitive ELISA-based assay for quantification of allergen-specific IgE antibody levels
- PMID: 32302409
- PMCID: PMC7687237
- DOI: 10.1111/all.14325
Highly sensitive ELISA-based assay for quantification of allergen-specific IgE antibody levels
Conflict of interest statement
RV has received research grants from HVD Life Sciences, Vienna, Austria and Viravaxx, Vienna, Austria, and serves as consultant for Viravaxx. MvH has received lecture fees from Thermo Fisher Scientific and consultancy fees from Biomay AG, Vienna, Austria, and Hycor Biomedical LLC, CA, US, outside of the submitted work. Other authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
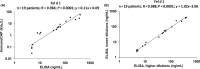
Figures

References
-
- Anto JM, Bousquet J, Akdis M, et al. Mechanisms of the Development of Allergy (MeDALL): Introducing novel concepts in allergy phenotypes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139:388‐399. - PubMed
-
- Grönlund H, Adédoyin J, Reininger R, et al. Higher immunoglobulin E antibody levels to recombinant Fel d 1 in cat‐allergic children with asthma compared with rhinoconjunctivitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008;38:1275‐1281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

