Dermal Adipocyte Lipolysis and Myofibroblast Conversion Are Required for Efficient Skin Repair
- PMID: 32302523
- PMCID: PMC7853423
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.03.013
Dermal Adipocyte Lipolysis and Myofibroblast Conversion Are Required for Efficient Skin Repair
Abstract
Mature adipocytes store fatty acids and are a common component of tissue stroma. Adipocyte function in regulating bone marrow, skin, muscle, and mammary gland biology is emerging, but the role of adipocyte-derived lipids in tissue homeostasis and repair is poorly understood. Here, we identify an essential role for adipocyte lipolysis in regulating inflammation and repair after injury in skin. Genetic mouse studies revealed that dermal adipocytes are necessary to initiate inflammation after injury and promote subsequent repair. We find through histological, ultrastructural, lipidomic, and genetic experiments in mice that adipocytes adjacent to skin injury initiate lipid release necessary for macrophage inflammation. Tamoxifen-inducible genetic lineage tracing of mature adipocytes and single-cell RNA sequencing revealed that dermal adipocytes alter their fate and generate ECM-producing myofibroblasts within wounds. Thus, adipocytes regulate multiple aspects of repair and may be therapeutic for inflammatory diseases and defective wound healing associated with aging and diabetes.
Keywords: cellular plasticity; dermal adipose tissue; inflammation; lipolysis; myofibroblast; wound healing.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors have no competing interests.
Figures
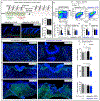
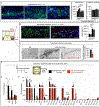


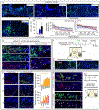


Comment in
-
Skinny Fat Cells Stimulate Wound Healing.Cell Stem Cell. 2020 Jun 4;26(6):801-803. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.04.021. Cell Stem Cell. 2020. PMID: 32502400
References
-
- Alvarez-Curto E, and Milligan G (2016). Metabolism meets immunity: The role of free fatty acid receptors in the immune system. Biochemical Pharmacology 114, 3–13. - PubMed
-
- Barrientos S, Stojadinovic O, Golinko MS, Brem H, and Tomic-Canic M (2008). Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound Repair and Regeneration 16, 585–601. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Drai D, Elmer G, Kafkafi N, and Golani I (2001). Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior genetics research. Behav. Brain Res 125, 279–284. - PubMed
-
- Berndt J, Kralisch S, Klöting N, Ruschke K, Kern M, Fasshauer M, Schön M, Stumvoll M, and Blüher M (2008). Adipose Triglyceride Lipase Gene Expression in Human Visceral Obesity. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 116, 203–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

