The epitranscriptomic writer ALKBH8 drives tolerance and protects mouse lungs from the environmental pollutant naphthalene
- PMID: 32303148
- PMCID: PMC7518688
- DOI: 10.1080/15592294.2020.1750213
The epitranscriptomic writer ALKBH8 drives tolerance and protects mouse lungs from the environmental pollutant naphthalene
Abstract
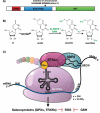
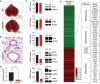
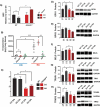
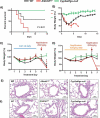
The epitranscriptomic writer Alkylation Repair Homolog 8 (ALKBH8) is a transfer RNA (tRNA) methyltransferase that modifies the wobble uridine of selenocysteine tRNA to promote the specialized translation of selenoproteins. Using Alkbh8 deficient (Alkbh8def) mice, we have investigated the importance of epitranscriptomic systems in the response to naphthalene, an abundant polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and environmental toxicant. We performed basal lung analysis and naphthalene exposure studies using wild type (WT), Alkbh8def and Cyp2abfgs-null mice, the latter of which lack the cytochrome P450 enzymes required for naphthalene bioactivation. Under basal conditions, lungs from Alkbh8def mice have increased markers of oxidative stress and decreased thioredoxin reductase protein levels, and have reprogrammed gene expression to differentially regulate stress response transcripts. Alkbh8def mice are more sensitive to naphthalene induced death than WT, showing higher susceptibility to lung damage at the cellular and molecular levels. Further, WT mice develop a tolerance to naphthalene after 3 days, defined as resistance to a high challenging dose after repeated exposures, which is absent in Alkbh8def mice. We conclude that the epitranscriptomic writer ALKBH8 plays a protective role against naphthalene-induced lung dysfunction and promotes naphthalene tolerance. Our work provides an early example of how epitranscriptomic systems can regulate the response to environmental stress in vivo.
Keywords: ALKBH8; Epitranscriptomics; RNA modification; naphthalene; selenoprotein; stress response; tolerance; translation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Selenoproteins and the senescence-associated epitranscriptome.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 Dec;247(23):2090-2102. doi: 10.1177/15353702221116592. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 36036467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epitranscriptomic Reprogramming Is Required to Prevent Stress and Damage from Acetaminophen.Genes (Basel). 2022 Feb 25;13(3):421. doi: 10.3390/genes13030421. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35327975 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of epitranscriptomic control of selenocysteine utilization engages senescence and mitochondrial reprogramming☆.Redox Biol. 2020 Jan;28:101375. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101375. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 31765888 Free PMC article.
-
tRNA modification enzyme-dependent redox homeostasis regulates synapse formation and memory.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 12;121(46):e2317864121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2317864121. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39495910 Free PMC article.
-
Epitranscriptomic systems regulate the translation of reactive oxygen species detoxifying and disease linked selenoproteins.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Nov 1;143:573-593. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.08.030. Epub 2019 Aug 30. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31476365 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Arsenite toxicity is regulated by queuine availability and oxidation-induced reprogramming of the human tRNA epitranscriptome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Sep 20;119(38):e2123529119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2123529119. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36095201 Free PMC article.
-
Selenoproteins and the senescence-associated epitranscriptome.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 Dec;247(23):2090-2102. doi: 10.1177/15353702221116592. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 36036467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epitranscriptomic Reprogramming Is Required to Prevent Stress and Damage from Acetaminophen.Genes (Basel). 2022 Feb 25;13(3):421. doi: 10.3390/genes13030421. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35327975 Free PMC article.
-
Dysfunctional tRNA reprogramming and codon-biased translation in cancer.Trends Mol Med. 2022 Nov;28(11):964-978. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2022.09.007. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Trends Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36241532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Coping Mechanisms: Reprogramming tRNAs To Regulate Codon-Biased Translation of Stress Response Proteins.Acc Chem Res. 2023 Dec 5;56(23):3504-3514. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00572. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Acc Chem Res. 2023. PMID: 37992267 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
