Novel insight into the regulatory roles of diverse RNA modifications: Re-defining the bridge between transcription and translation
- PMID: 32303268
- PMCID: PMC7164178
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-020-01194-6
Novel insight into the regulatory roles of diverse RNA modifications: Re-defining the bridge between transcription and translation
Abstract
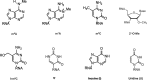
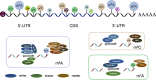
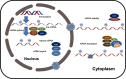
RNA modifications can be added or removed by a variety of enzymes that catalyse the necessary reactions, and these modifications play roles in essential molecular mechanisms. The prevalent modifications on mRNA include N6-methyladenosine (m6A), N1-methyladenosine (m1A), 5-methylcytosine (m5C), 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (hm5C), pseudouridine (Ψ), inosine (I), uridine (U) and ribosemethylation (2'-O-Me). Most of these modifications contribute to pre-mRNA splicing, nuclear export, transcript stability and translation initiation in eukaryotic cells. By participating in various physiological processes, RNA modifications also have regulatory roles in the pathogenesis of tumour and non-tumour diseases. We discussed the physiological roles of RNA modifications and associated these roles with disease pathogenesis. Functioning as the bridge between transcription and translation, RNA modifications are vital for the progression of numerous diseases and can even regulate the fate of cancer cells.
Keywords: RNA modifications; diseases; m1A; m5C; m6A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Davis FF, Allen FW. Ribonucleic acids from yeast which contain a fifth nucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1957;227:907–915. - PubMed
-
- Cohn WE. Pseudouridine, a carbon-carbon linked ribonucleoside in ribonucleic acids: isolation, structure, and chemical characteristics. J Biol Chem. 1960;235:1488–1498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

