Mitochondrial Metabolism in Acute Kidney Injury
- PMID: 32303274
- PMCID: PMC7282287
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2020.01.002
Mitochondrial Metabolism in Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
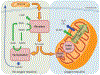
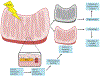
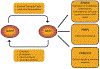
The kidney is a highly metabolic organ that requires substantial adenosine triphosphate for the active transport required to maintain water and solute reabsorption. Aberrations in energy availability and energy utilization can lead to cellular dysfunction and death. Mitochondria are essential for efficient energy production. The pathogenesis of acute kidney injury is complex and varies with different types of injury. However, multiple distinct acute kidney injury syndromes share a common dysregulation of energy metabolism. Pathways of energy metabolism and mitochondrial dysfunction are emerging as critical drivers of acute kidney injury and represent new potential targets for treatment. This review shows the basic metabolic pathways that all cells depend on for life; describes how the kidney optimizes those pathways to meet its anatomic, physiologic, and metabolic needs; summarizes the importance of metabolic and mitochondrial dysfunction in acute kidney injury; and analyzes the mitochondrial processes that become dysregulated in acute kidney injury including mitochondrial dynamics, mitophagy, mitochondrial biogenesis, and changes in mitochondrial energy metabolism.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; metabolism; mitochondria.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement:
Samir M. Parikh is listed as an inventor on patent filings from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, holds equity in Raksana Therapeutics, and has received consulting fees from Astellas, Cytokinesis, Mission Therapeutics, and Aerpio, where he serves on the Scientific Advisory Board.
Figures

References
-
- Harris SI, Balaban RS, Mandel LJ. Oxygen consumption and cellular ion transport: evidence for adenosine triphosphate to O2 ratio near 6 in intact cell. Science. 1980;208:1148–50. - PubMed
-
- Kurnik BR, Weisberg LS, Kurnik PB. Renal and systemic oxygen consumption in patients with normal and abnormal renal function. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992;2:1617–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

