COVID-19 and immunomodulation in IBD
- PMID: 32303609
- PMCID: PMC7211083
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321269
COVID-19 and immunomodulation in IBD
Abstract
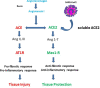
The current coronavirus pandemic is an ongoing global health crisis due to COVID-19, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Although COVID-19 leads to little or mild flu-like symptoms in the majority of affected patients, the disease may cause severe, frequently lethal complications such as progressive pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome and organ failure driven by hyperinflammation and a cytokine storm syndrome. This situation causes various major challenges for gastroenterology. In the context of IBD, several key questions arise. For instance, it is an important question to understand whether patients with IBD (eg, due to intestinal ACE2 expression) might be particularly susceptible to COVID-19 and the cytokine release syndrome associated with lung injury and fatal outcomes. Another highly relevant question is how to deal with immunosuppression and immunomodulation during the current pandemic in patients with IBD and whether immunosuppression affects the progress of COVID-19. Here, the current understanding of the pathophysiology of COVID-19 is reviewed with special reference to immune cell activation. Moreover, the potential implications of these new insights for immunomodulation and biological therapy in IBD are discussed.
Keywords: cytokines; inflammation; inflammatory bowel disease.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


Comment in
-
Infliximab for severe ulcerative colitis and subsequent SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: a stone for two birds.Gut. 2021 Mar;70(3):623-624. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321760. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Gut. 2021. PMID: 32554621 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
