The prevention and management of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in radiology departments in epidemic areas
- PMID: 32306166
- PMCID: PMC7165252
- DOI: 10.1007/s11604-020-00974-w
The prevention and management of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in radiology departments in epidemic areas
Abstract
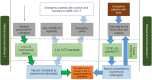
This review based on the actual results of epidemic prevention management in radiology departments in epidemic areas, and using designated hospital management methods, to summarize the radiology protection system. With the cooperation of the whole hospital and radiology department, a number of effective evaluation methods have been carried out to ensure the optimization of clinical protection. These practical methods provide a basis for the further promotion of management strategies and reduction of nosocomial infection. To our knowledge, the establishment of standardized protection and clear process has opened up a new idea of epidemic prevention management, which can effectively provide timely, efficient, and accurate support for clinical research, and promote the transformation from clinical research type to scientific research management type.
Keywords: Hospital management; Novel coronavirus; Pneumonia epidemic; Prevention.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- China National Health Commission. Diagnosis and treatment of 2019-nCoV pneumonia in China. In Chinese (Provisional 7th Edition). 2020. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7652m/202003/a31191442e29474b98bfed5579d5af.... Accessed 6 Mar 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources