Attenuation of Murine Collagen-Induced Arthritis by Targeting CD6
- PMID: 32307907
- PMCID: PMC7745675
- DOI: 10.1002/art.41288
Attenuation of Murine Collagen-Induced Arthritis by Targeting CD6
Abstract
Objective: CD6 is an important regulator of T cell function that interacts with the ligands CD166 and CD318. To further clarify the significance of CD6 in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), we examined the effects of targeting CD6 in the mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA), using CD6-knockout (CD6-KO) mice and CD6-humanized mice that express human CD6 in lieu of mouse CD6 on their T cells.
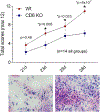
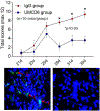
Methods: We immunized wild-type (WT) and CD6 gene-KO mice with a collagen emulsion to induce CIA. For treatment studies using CD6-humanized mice, mice were immunized similarly and a mouse anti-human CD6 IgG (UMCD6) or control IgG was injected on days 7, 14, and 21. Joint tissues were evaluated for tissue damage, leukocyte infiltration, and local inflammatory cytokine production. Collagen-specific Th1, Th9, and Th17 responses and serum levels of collagen-specific IgG subclasses were also evaluated in WT and CD6-KO mice with CIA.
Results: The absence of CD6 reduced 1) collagen-specific Th9 and Th17, but not Th1 responses, 2) the levels of many proinflammatory joint cytokines, and 3) serum levels of collagen-reactive total IgG and IgG1, but not IgG2a and IgG3. Joint homogenate hemoglobin content was significantly reduced in CD6-KO mice with CIA compared to WT mice with CIA (P < 0.05) (reduced angiogenesis). Moreover, treating CD6-humanized mice with mouse anti-human CD6 monoclonal antibody was similarly effective in reducing joint inflammation in CIA.
Conclusion: Taken together, these data suggest that interaction of CD6 with its ligands is important for the perpetuation of CIA and other inflammatory arthritides that are T cell driven.
© 2020, American College of Rheumatology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: none
Figures
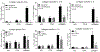
References
-
- Gangemi RM, Swack JA, Gaviria DM, Romain PL. Anti-T12, an anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody, can activate human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989;143(8):2439–47. - PubMed
-
- Consuegra-Fernandez M, Lin F, Fox DA, Lozano F. Clinical and experimental evidence for targeting CD6 in immune-based disorders. Autoimmun Rev. 2018;17(5):493–503. - PubMed
-
- Osorio LM, Ordonez C, Garcia CA, Jondal M, Chow SC. Evidence for protein tyrosine kinase involvement in CD6-induced T cell proliferation. Cell Immunol. 1995;166(1):44–52. - PubMed
-
- Hem CD, Ekornhol M, Granum S, Sundvold-Gjerstad V, Spurkland A. CD6 and Linker of Activated T Cells are Potential Interaction Partners for T Cell-Specific Adaptor Protein. Scand J Immunol. 2017;85(2):104–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

